Question 1
Environment | Conservation | Easy | NCERT
SOURCE
Which of the following is correctly related to Project Tiger. It was
A. Started in 1973
B. Started in 1979
C. Started in 1984
D. Launched for management of Tiger habitats
E. Started in 1994
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. (B) and (D) only
B. (C) and (D) only
C. (D) and (E) only
D. (A) and (D) only
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) (A) and (D) only
Detailed Explanation
- Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation movement initiated in India to protect the endangered tiger.
- The project was initiated in 1973 by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of the Government of India.
- As of March 2025, there are 58 protected areas that have been designated as tiger reserves under the project.
Question 2
Environment | Species Growth | Easy | NCERT
SOURCE
Arrange the phases of logistics population growth form starting from 1st to last:
A. Plateau phase
B. Exponential phase
C. Positive Acceleration phase
D. Lag phase
E. Negative Acceleration phase
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. C, B, D, E, A
B. D, B, E, A, C
C. C, D, A, B, E
D. D, C, B, E, A
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) C, D, A, B, E
Detailed Explanation
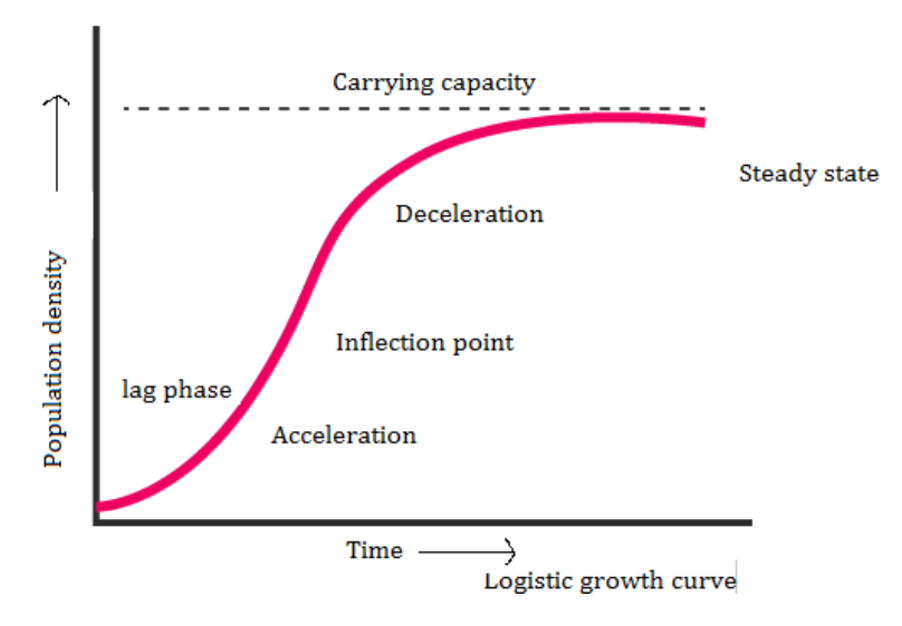
- Logistic growth: No population of any species in nature has at its disposal unlimited resources to permit exponential growth. This leads to competition between individuals for limited resources.
- Eventually, the ‘fittest’ individual will survive and reproduce. In nature, a given habitat has enough resources to support a maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. Let us call this limit as nature’s carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat.
- A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows initially a lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote, when the population density reaches the carrying capacity.
- Logistic growth is characterized by an S-shaped (sigmoid) curve on a graph, showing an initial slow growth phase, followed by rapid growth, and then a levelling off as the population approaches the environment’s carrying capacity.
Question 3
Economy | Basics | Easy | NCERT
SOURCE
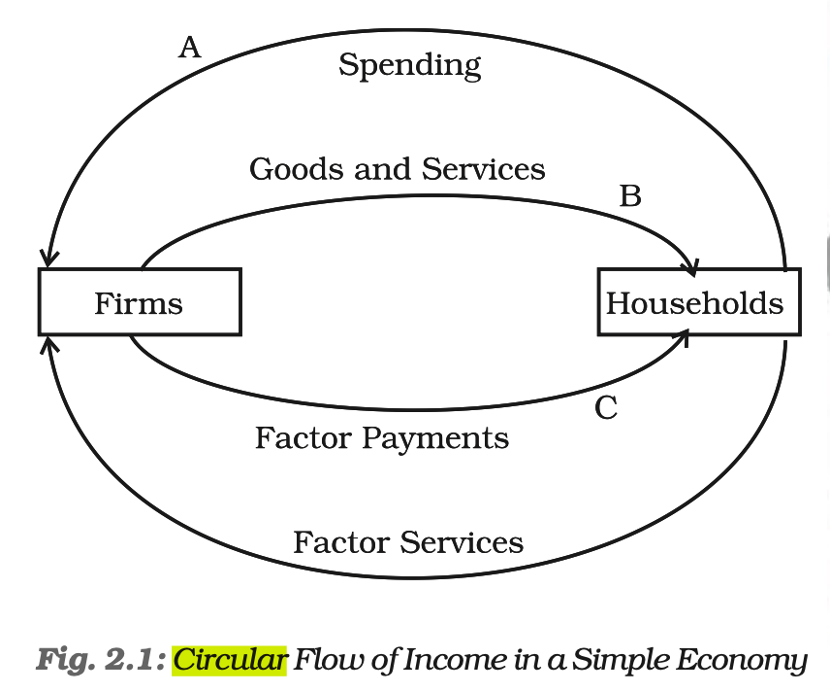
Identify the correct statement in the context of Circular Flow of Income in a two sector economy :
A. The household receives factor services from firms.
B. Household invests while firm saves.
C. Firms produce goods and services.
D. Household supplies factor services to the Government
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Firms produce goods and services.
Detailed Explanation
- The firm receives factor services from the household sector.
- The household invests while the firm produces goods and services. There is no savings or leakages
- Firms produce goods and services.
- Household supplies factor services to the firm. The Government is not involved in the two-sector economy.
Question 4
Economy | Institutions | Easy | NCERT
SOURCE
Choose the correct chronological sequence in ascending order (earliest to latest) :
A. Establishment of NABARD
B. FRBMA (Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act)
C. Third Five Year Plan
D. Nationalization of RBI
A. (A), (B), (C), (D)
B. (A), (C), (B), (D)
C. (D), (A), (B), (C)
D. (D), (C), (A), (B)
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) (D), (C), (A), (B)
Detailed Explanation
- Establishment of NABARD – NABARD came into existence on 12 July 1982 by transferring the agricultural credit functions of RBI and refinance functions of the then Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation (ARDC). It was dedicated to the service of the nation by the late Prime Minister Smt. Indira Gandhi on 05 November 1982.
- FRBMA (Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act) – An Act of 2003 to provide for the responsibility of the Central Government to ensure intergenerational equity in fiscal management and long-term macro-economic stability by removing fiscal impediments in the effective conduct of monetary policy and prudential debt management consistent with fiscal sustainability through limits on the Central Government borrowings, debt and deficits, greater transparency in fiscal operations of the Central Government and conducting fiscal policy in a medium-term framework and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- Third Five Year Plan – The Third Five-Year Plan in India (1961-1966) aimed to achieve self-sufficiency in food grains and establish a self-reliant economy. It focused on boosting agricultural and industrial production, but faced unforeseen challenges including wars with China and Pakistan, and severe droughts, hindering its progress.
- Nationalization of RBI – The Reserve Bank of India was nationalised with effect from 1st January, 1949 on the basis of the Reserve Bank of India (Transfer to Public Ownership) Act, 1948. All shares in the capital of the Bank were deemed transferred to the Central Government on payment of a suitable compensation.
Question 5
History | Indus Valley Civilisation | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Choose the correct statements regarding residential buildings at Mohenjodaro.
A. The main entrance gave a direct view of the interior or the courtyard.
B. Courtyard with rooms on all sides.
C. No concept of staircase.
D. No windows were there in the walls along the ground level.
E. Houses did not have their own bathroom.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A. (A), (B) Only
B. (B), (C) Only
C. (B), (D) Only
D. (D), (E) Only
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) (B), (D) Only
Detailed Explanation
- The Lower Town at Mohenjodaro provides examples of residential buildings.
- Many were centred on a courtyard, with rooms on all sides.
- The courtyard was probably the centre of activities such as cooking and weaving, particularly during hot and dry weather.
- There are no windows in the walls along the ground level.
- The main entrance does not give a direct view of the interior or the courtyard.
- Every house had its own bathroom paved with bricks, with drains connected through the wall to the street drains.
- Some houses have remains of staircases to reach a second storey or the roof.
- Many houses had wells, often in a room that could be reached from the outside and perhaps used by passers-by.
- Scholars have estimated that the total number of wells in Mohenjodaro was about 700.
Question 6
History | Mahajanapadas | Easy | NCERT
SOURCE
Identify the correct pair of Mahajanapadas.
A. Vajji, Magadha, Avanti, Banawali
B. Magadha, Koshala, Kuru, Panchala
C. Gandhara, Afghan, Magadha, Koshala
D. Matsya, Chola, Chera, Pandya
E. Vatsa, Chedi, Gandhara, Avanti
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. (B), (E) Only
B. (C), (A) Only
C. (D), (A) Only
D. (E), (C) Only
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) (B), (E) Only
Detailed Explanation
- The 16 Mahajanapadas, ancient Indian kingdoms, were: Kasi, Kosala, Anga, Magadha, Vajji, Malla, Chedi, Vatsa, Kuru, Panchala, Matsya, Surasena, Assaka, Avanti, Gandhara, and Kamboja.
Question 7
Polity | Formation of States | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Arrange the following events related to creation of new states in chronological order.
A. Demarcation of boundaries of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh
B. Formation of Andhra on linguistic lines
C. Creation of Himachal Pradesh on the basis of geographical zones
D. Formation of Maharashtra and Gujarat
E. Formation of Meghalaya
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A. (B), (D), (C), (E), (A)
B. (B), (C), (D), (A), (E)
C. (A), (D), (C), (E), (B)
D. (C), (B), (D), (E), (A)
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) (B), (D), (C), (E), (A)
Detailed Explanation
- The Prime Minister announced the formation of a separate Andhra state in December 1952.
- There was an experiment of ‘bilingual’ Bombay state, consisting of Gujarati- and Marathi-speaking people. After a popular agitation, the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat were created in 1960.
- In Punjab also, there were two linguistic groups: Hindi-speaking and Punjabi-speaking. The Punjabi-speaking people demanded a separate state. But it was not granted with other states in 1956. Statehood for Punjab came ten years later, in 1966, when the territories of today’s Haryana and Himachal Pradesh were separated from the larger Punjab state.
- Another major reorganisation of states took place in the north-east in 1972. Meghalaya was carved out of Assam in 1972. Manipur and Tripura too emerged as separate states in the same year.
- Sub-regions raised demands for separate states on the basis of a separate regional culture or complaints of regional imbalance in development. Three such states, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand and Jharkhand, were created in 2000.
Question 8
Polity | LPG | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Statement I : The Second Five Year Plan stressed on heavy industries.
Statement II : A bulk of industries like electricity, railways, steel could be developed by the private sector.
A. Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
B. Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
C. Statement I is correct, but Statement II is incorrect
D. Statement I is incorrect, but Statement II is correct
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Statement I is correct, but Statement II is incorrect
Detailed Explanation
- The Second FYP stressed on heavy industries. It was drafted by a team of economists and planners under the leadership of P. C. Mahalanobis.
- The government imposed substantial tariffs on imports in order to protect domestic industries. Such a protected environment helped both public and private sector industries to grow. As savings and investment were growing in this period, a bulk of these industries like electricity, railways, steel, machineries and communication could be developed in the public sector.
Question 9
Geography | Copper Mines | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
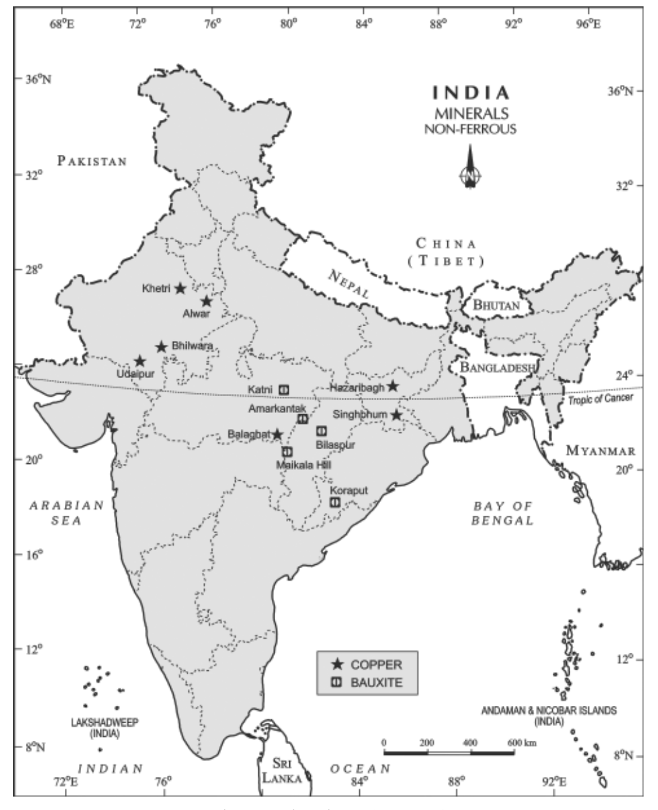
Arrange the following copper mines in North to South direction :
A. Alwar
B. Bhilwara
C. Khetri
D. Udaipur
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A. (B), (D), (C), (A)
B. (C), (B), (A), (D)
C. (B), (C), (D), (A)
D. (C), (A), (B), (D)
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) (C), (A), (B), (D)
Detailed Explanation
Question 10
Geography | Drainage System | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Arrange the following river basins in descending order according to their size.
A. Mahanadi
B. Godavari
C. Ganga
D. Pennar
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. (C), (B), (D), (A)
B. (B), (C), (A), (D)
C. (B), (A), (D), (C)
D. (C), (B), (A), (D)
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) (C), (B), (A), (D)
Detailed Explanation
- The Mahanadi River Basin is the 8th largest river basin in India, covering a total area of approximately 141,600 km² and extending across five states: Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh. Originating in Chhattisgarh, the Mahanadi River flows through Odisha to the Bay of Bengal, acting as a lifeline for the region by providing water for agriculture, flood control, and supporting significant industries.
- The Godavari River basin is India’s second-largest river basin, covering over 3. 1 million sq. km across several states, including Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha, with smaller portions in other states. It originates in the Western Ghats near Nashik, Maharashtra, and flows eastward to the Bay of Bengal. Bounded by hills and ranges, the basin features a tropical climate, with the Southwest monsoon providing most of the annual rainfall, supporting agriculture and river flow.
- The Ganga basin is spread over India, Tibet (China), Nepal and Bangladesh over a total area of 10,86,000 Sq.km. The major part of the geographical area of the Ganga basin lies in India and it is the biggest river basin in the country draining an area of 8,61,452 Sq.km which is slightly more than one-fourth (26. 3 %) of the total geographical area of the country. In India, it covers states of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh and Delhi.
- The Pennar Basin is a river drainage area in Peninsular India, encompassing parts of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, covering an area of about 55,213 square kilometers. It is defined by the Erramala, Nallamala,Velikonda, and Nandidurg hill ranges and the Krishna Basin on its boundaries. The basin is characterized by a dry tropical monsoon climate, supporting agriculture and small-scale industries like cotton weaving.





