Questions from Crash Course
1. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Ecophene in long term leads to Ecotype.
- Two ecospecies can produce viable off-springs while the ecophenes and ecotypes cannot.
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both are Correct
D. None is Correct
2. The destructive effect that the bread mould Penicillium has upon certain bacteria, is an example of:
A. Mutualism
B. Commensalism
C. Amensalism
D. Parasitism
Questions from Test Series
Foundation Test – 5 (Environment)
3. It is the species whose presence or absence or abundance reflects the environmental condition.
They serve as early warning mechanism or signals because they are sensitive to environmental conditions.
This is the best description of which species.
A. Keystone Species
B. Flagship Species
C. Foundation Species
D. Sentinel Species
4. Consider the following pairs:
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
| Biotic Interactions | Example |
| Predation | Varroa mite feeding on honeybees |
| Competition | Plants in evergreen forest |
| Parasitism | Cattle egret and grazing cattle |
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 only
D. 1 and 3 only
UPSC Previous Year Question 2016
5. With reference to an initiative called ‘The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is an initiative hosted by UNEP, IMF and World Economic Forum.
- It is a global initiative that focuses on drawing attention to the economic benefits of biodiversity.
- It presents an approach that can help decisionmakers recognize, demonstrate and capture the value of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answers with Explanations
Questions from Crash Course
1. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Ecophene in long term leads to Ecotype.
- Two ecospecies can produce viable off-springs while the ecophenes and ecotypes cannot.
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both are Correct
D. None is Correct
Answer: A
Explanation
Ecophene

- These are otherwise called Ecads or morphologically-changed forms.
- When a species is transported to a new environment, its first response will be to develop abilities to survive there.
- These differences among ecophenes are not permanent.
- They are just temporary variations to survive the new conditions.
- This reversibility is because there has been no change in the genetics of the two separate ecophenes.
- Therefore, ecophenes from different habitats, when brought together, become similar.
Ecotype
- However, if two of these ecophenes were to remain in their new habitat for too long, these morphological (physical) changes will start becoming permanent.
- This permanence in the adaptations arises due to changes in genes.
- Two ecotypes of an organism will show minor variations in their genetic stock.
Ecospecies
- Now, if two ecotypes have been separated from each other for a very long time.
- The adaptations become a permanent part of the genes.
- They are still the same species, but their difference physically and genetically are very distinct.
- In fact, two ecospecies cannot produce viable off-springs (which the ecophenes and ecotypes can).
- These ecospecies, left alone for many, many generations, then develop sufficient changes in them to become a separate species.
2. The destructive effect that the bread mould Penicillium has upon certain bacteria, is an example of:
A. Mutualism
B. Commensalism
C. Amensalism
D. Parasitism
Answer: C
Explanation
Mutualism
- This interaction confers benefits on both the interacting species.
- Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesising algae or cyanobacteria.
- Similarly, the mycorrhizae are associations between fungi and the roots of higher plants.
- The fungi help the plant in the absorption of essential nutrients from the soil while the plant in turn provides the fungi with energy-yielding carbohydrates.

- The most spectacular and evolutionarily fascinating examples of mutualism are found in plant animal relationships.
- Plants need the help of animals for pollinating their flower.
- Plants offer rewards or fees in the form of pollen and nectar for pollinators and juicy and nutritious fruits for seed dispersers and dispersing their seeds.
Commensalism
- This is the interaction in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- An orchid growing as an epiphyte on a mango branch,
- Barnacles growing on the back of a whale,
- The cattle egret and grazing cattle,
- Interaction between sea anemone that has stinging tentacles and the clown fish, etc


Amensalism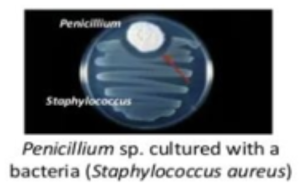
- An association between organisms of two different species in which one is inhibited or destroyed and the other is unaffected.
- An example is the destructive effect that the bread mold Penicillium has upon certain bacteria; the secretion, known as penicillin, has become a potent medicine in combating bacterial infections.
- Another example is the black walnut (Juglans nigra), which secretes juglone, a substance that destroys many herbaceous plants within its root zone.
Parasitism
- Considering that the parasitic mode of life ensures free lodging and meals, it is not surprising that parasitism has evolved in so many taxonomic groups from plants to higher vertebrates.
- Many parasites have evolved to be host-specific (they can parasitise only a single species of host) in such a way that both host and the parasite tend to co-evolve.
- Parasites have evolved special adaptations such as the loss of unnecessary sense organs, presence of adhesive organs or suckers to cling on to the host, loss of digestive system and high reproductive capacity.
- The life cycles are complex, involving one or two intermediate hosts or vectors to facilitate parasitisation of its primary host.
Questions from Test Series
Foundation Test – 5 (Environment)
3. It is the species whose presence or absence or abundance reflects the environmental condition.
They serve as early warning mechanism or signals because they are sensitive to environmental conditions.
This is the best description of which species.
A. Keystone Species
B. Flagship Species
C. Foundation Species
D. Sentinel Species
Answer: D
Explanation
Indicator/Sentinel Species
- It is the one who’s presence or absence or abundance reflects the environmental condition.
- They serve as early warning mechanism or signals because they are sensitive to environmental conditions.
- Also Known as Sentinel Species.
- Eg. Frogs, lichens, salmon
Keystone species
- Keystone species is a species whose addition to or loss from an ecosystem leads to major changes in the occurrence of at least one other species.
- Certain species in an ecosystem is considered more important in determining the presence of many other species in that ecosystem.
- All top predators (Tiger, Lion, Crocodile, Elephant) are considered as keystone species because they regulate all other animal population indirectly.
- Hence top predators are given much consideration in conservation.
- If keystone species is lost, it will result in the degradation of the whole ecosystem.
Foundation species
- Foundation species is a dominant primary producer in an ecosystem both in terms of abundance and influence.
- Example: kelp in kelp forests and corals in coral reefs.
Flagship species
- A flagship species is a species chosen to represent an environmental cause, such as an ecosystem in need of conservation.
- These species are chosen for their vulnerability, attractiveness or distinctiveness in order to engender support and acknowledgement from the public at large.
- Example: Indian tiger, African elephant, giant panda of China, the leatherback sea turtle, etc.
4. Consider the following pairs:
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
| Biotic Interactions | Example |
| Predation | Varroa mite feeding on honeybees |
| Competition | Plants in evergreen forest |
| Parasitism | Cattle egret and grazing cattle |
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 only
D. 1 and 3 only
Answer: C
Explanation
- In nature, animals, plants and microbes do not and cannot live in isolation but interact in various ways to form a biological community. Even in minimal communities, many interactive linkages exist, although all may not be readily apparent. Interspecific interactions arise from the interaction of populations of two different species.
- They could be beneficial, detrimental or neutral (neither harm nor benefit) to one of the species or both.
- Predation, parasitism and commensalism share a common characteristic– the interacting species live closely together.
- Predation- One species benefits and the other is harmed. It is nature’s way of transferring to higher trophic levels the energy fixed by plants. Example Pitcher plant consuming insect. Pair 1 is incorrectly matched.
- The Varroa mite, or Varroa destructor, is a parasitic insect that attacks and feeds on honeybees. Reddish-brown in colour, the tiny pests are known to kill entire colonies of honeybees.
- They often travel from bee to bee and also via beekeeping equipment, such as combs that have been extracted. The spread of the mite is largely blamed for a sharp decline in the number of honey-bee colonies worldwide. It has plundered bee colonies across the globe
- Competition- It is generally believed that competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting. Example: Plants in the evergreen forests are fighting for sunlight, which negatively affects their growth. It is an example of competitive interaction where plants are competing for the same source i.e. sunlight. Pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Commensalism- One species benefits and the other is unaffected. The egrets always forage close to where the cattle are grazing. Cattle egrets eat the flies and bugs that tender to bother the cattle. The movement of livestock also dislodges various insects on which cattle egrets feed on. So, this is called commensalism in which the egrets benefits and this has no effect on Cattle. Pair 3 is incorrectly matched.
UPSC Previous Year Question 2016
5. With reference to an initiative called ‘The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is an initiative hosted by UNEP, IMF and World Economic Forum.
- It is a global initiative that focuses on drawing attention to the economic benefits of biodiversity.
- It presents an approach that can help decisionmakers recognize, demonstrate and capture the value of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation
- The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) is a global initiative focused on “making nature’s values visible”.
- Its principal objective is to mainstream the values of biodiversity and ecosystem services into decision-making at all levels.
- It aims to achieve this goal by following a structured approach to valuation that helps decision-makers recognize the wide range of benefits provided by ecosystems and biodiversity, demonstrate their values in economic terms and, where appropriate, capture those values in decision-making.
➡️UPSC 2023 General Studies Course: https://sleepyclasses.com/general-studies-for-upsc/
➡️Sociology Optional for UPSC : https://sleepyclasses.com/sociology-for-upsc/
➡️Political Science and IR for UPSC: https://sleepyclasses.com/psir-for-upsc/
➡️Signup here – https://sleepyclasses.com/
Have any query related to UPSC preparation: 📞Contact Us ► Toll-Free: 1800 890 3043 ► Mobile: 6280133177 ► Email: Sleepy.Classes@gmail.com ► WhatsApp: 6280133177



