Questions from Crash Course
PRELIMS CRASH COURSE ( Mains – 2018)
1. Which of the Following is true about Mantle Plumes?
- The mantle plume provides a continuous supply of abnormally hot magma to a fixed location in the mantle referred to as a hotspot.
- Most of the mantle plumes lie far from tectonic plate boundaries (e.g. Hawaiian Hotspot), while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries (e.g. Iceland Hotspot).
- On the continents, mantle plumes have been responsible for extensive accumulations of flood basalts.
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
PRELIMS CRASH COURSE – NCERT based statements
2. Choose the incorrect statements :
A. Water vapour is a variable gas in the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude.
B. In the warm and wet tropics, it may account for four per cent of the air by volume, while in the dry and cold areas of desert and polar regions, it may be less than one per cent of the air.
C. Water vapour also increases from the equator towards the poles.
D. It also absorbs parts of the insolation from the sun and preserves the earth’s radiated heat and thus acts like a blanket allowing the earth neither to become too cold nor too hot.
Questions from Test Series
Foundation Tests
Prelims Test Series – Test 2 – Geography -1
3. This landform is formed when streams flowing from higher levels break into foot slope plains of low gradient. Normally very coarse load is carried by streams flowing over mountain slopes. This load becomes too heavy for the streams to be carried over gentler gradients and gets deposited at foot slopes.
Above passage is the best description of which of the following landforms:
A. Alluvial Fans
B. River Terraces
C. Deltas
D. Floodplains
4. Consider the following statements with reference to tides:
- The time between the high tide and low tide, when the water level is falling, is called the ebb.
- The time between the low tide and high tide, when the tide is rising, is called the flow or flood.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
UPSC Previous Year Question
Conceptual Question
5. Which one of the lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert?
A. Lake Victoria
B. Lake Faguibine
C. Lake Oguta
D. Lake Volta
Answers with Explanations
Questions from Crash Course
PRELIMS CRASH COURSE ( Mains – 2018)
1. Which of the Following is true about Mantle Plumes?
- The mantle plume provides a continuous supply of abnormally hot magma to a fixed location in the mantle referred to as a hotspot.
- Most of the mantle plumes lie far from tectonic plate boundaries (e.g. Hawaiian Hotspot), while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries (e.g. Iceland Hotspot).
- On the continents, mantle plumes have been responsible for extensive accumulations of flood basalts.
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
Explanation
Additional Information – Mantle Plumes
- Mantle plumes are large blobs of molten rock that rise towards the surface from the interiors of a planet.
- They push through the intermediate or mantle layers and accumulate at the base of the crust.
This geological phenomenon can be witnessed on Earth in Hawaii where the warm materials from the plume.
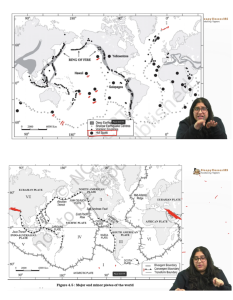

Hotspot Volcanism
- Hotspot volcanism is a type of volcanism that typically occurs at the interior parts of the lithospheric plates rather than at the zones of convergence and divergence (plate margins).
- The Iceland Hotspot and Afar Hotspot which are situated at the divergent boundary are exceptions.
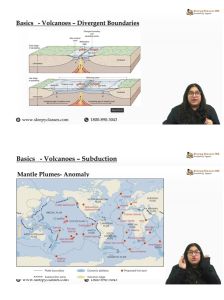
Mantle Plumes
- A mantle plume is the convection of abnormally hot rock (magma) within the Earth’s mantle.
- Unlike the larger convection cells in the mantle which change their position over geological timescales, the position of the mantle plumes seems to be relatively fixed.
- Mantle plumes are theorized to form at the core-mantle boundary where an abnormally hot plume of rock accumulates.
- The mantle plume is shaped like a mushroom with a long conduit (tail) connecting the bulbous head to its base. The head expands in size as the plume rises.
Mantle plumes and flood basalt volcanism (large igneous provinces)
- On the continents, mantle plumes have been responsible for extensive accumulations of flood basalts.
- When a plume head encounters the base of the lithosphere, it flattens out and undergoes widespread decompression melting to form large volumes of basalt magma.
- The basaltic magma may then erupt onto the surface through a series of fissures giving rise to large igneous provinces. When created, these regions often occupy several thousand square kilometers.
- Large igneous provinces, such as Iceland, Siberian Traps, Deccan Traps, and Ontong Java Plateau, are extensive regions of basalts on a continental scale resulting from flood basalt eruptions.
Mantle plumes and volcanic hotspots
- The mantle plume provides a continuous supply of abnormally hot magma to a fixed location in the mantle referred to as a hotspot.
- The melted rock, known as magma, which is at high pressure, often pushes through cracks in the crust to form hotspot volcanoes (e.g. Mount Mauna Kea).
Hotspot volcano chain
- A volcano above a hotspot does not erupt forever. Attached to the tectonic plate below, the volcano moves and is eventually cut off from the hotspot.
- Without any source of heat, the volcano becomes extinct and cools. This cooling causes the rock of the volcano and the tectonic plate to become denser. Over time, the dense rock sinks and erodes.
- The Hawaiian Islands chain in the Pacific Ocean is the best example.
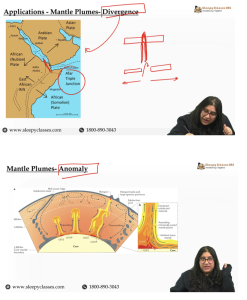
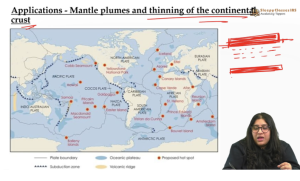
Mantle plumes and thinning of the continental crust
- The Yellowstone hotspot is an example for a hotspot developed beneath a continent.
- Here the mantle plume has been thinning the part of America’s crust (divergence of the plume exerts extensional stress on the lithospheric plate) above and is likely to thin the whole of the surface opening the door for the underlying supervolcano.
- Mantle plumes and uplifted landforms
- As the plume reaches the lithosphere, it spreads out laterally doming zones of the Earth. E.g. The Ethiopian Highlands.
- The Ethiopian Highlands began before the beginning of the Tertiary Period (66 mya), as the mantle plume below uplifted a broad dome of the ancient rocks of the Arabian-Nubian Shield.
- Around 30 million years ago, a flood basalt plateau began to form, piling layers upon layers of voluminous fissure-fed basaltic lava flows.
PRELIMS CRASH COURSE – NCERT based statements
2. Choose the incorrect statements :
A. Water vapour is a variable gas in the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude.
B. In the warm and wet tropics, it may account for four per cent of the air by volume, while in the dry and cold areas of desert and polar regions, it may be less than one per cent of the air.
C. Water vapour also increases from the equator towards the poles.
D. It also absorbs parts of the insolation from the sun and preserves the earth’s radiated heat and thus acts like a blanket allowing the earth neither to become too cold nor too hot.
Answer: C
Explanation
- Water vapour is a variable gas in the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude.
- In the warm and wet tropics, it may account for four per cent of the air by volume, while in the dry and cold areas of desert and polar regions, it may be less than one per cent of the air.
- Water vapour also increases from the equator towards the poles.
- It also absorbs parts of the insolation from the sun and preserves the earth’s radiated heat and thus acts like a blanket allowing the earth neither to become too cold nor too hot.
Questions from Test Series
Foundation Tests
Prelims Test Series – Test 2 – Geography -1
3. This landform is formed when streams flowing from higher levels break into foot slope plains of low gradient. Normally very coarse load is carried by streams flowing over mountain slopes. This load becomes too heavy for the streams to be carried over gentler gradients and gets deposited at foot slopes.
Above passage is the best description of which of the following landforms:
A. Alluvial Fans
B. River Terraces
C. Deltas
D. Floodplains
Answer: A
Explanation
This landform is formed when streams flowing from higher levels break into foot slope plains of low gradient 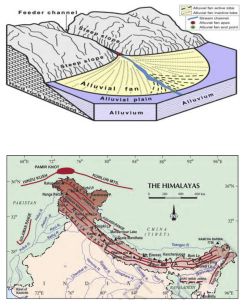
Normally very coarse load is carried by streams flowing over mountain slopes. This load becomes too heavy for the streams to be carried over gentler gradients and gets deposited at foot slopes.
- Alluvial Fans are formed when streams flowing from higher levels break into foot slope plains of low gradient. Normally a very coarse load is carried by streams flowing over mountain slopes. This load becomes too heavy for the streams to be carried over gentler gradients and gets dumped and spread as a broad low to high cone shaped deposit called alluvial fan.
- Usually, the streams which flow over fans are not confined to their original channels for long and shift their position across the fan forming many channels called distributaries. Alluvial fans in humid areas show normally low cones with gentle slope from head to toe and they appear as high cones with steep slope in arid and semi-arid climates.
4. Consider the following statements with reference to tides:
- The time between the high tide and low tide, when the water level is falling, is called the ebb.
- The time between the low tide and high tide, when the tide is rising, is called the flow or flood.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
Explanation

- Tides can be defined as the alternate rise and fall of the ocean water. It is caused by the combined effects of
- The gravitational force exerted on Earth by the Sun.
- The gravitational force exerted on Earth by the Moon.
- Rotation of the Earth.
- Statement 1 is correct: The time between the high tide and low tide, when the water level is falling, is called the ebb.
- Statement 2 is correct: The time between the low tide and high tide, when the tide is rising, is called the flow or flood.
UPSC Previous Year Question
Conceptual Question
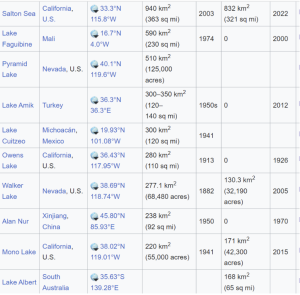
5. Which one of the lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert?
A. Lake Victoria
B. Lake Faguibine
C. Lake Oguta
D. Lake Volta
Answer: B
Explanation
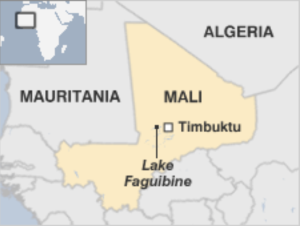
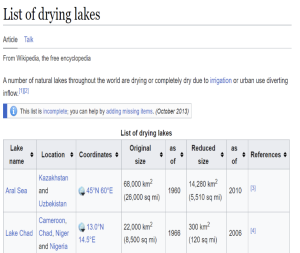
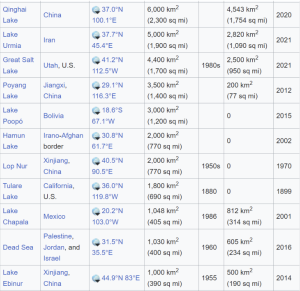
- Lake Faguibine in northern Mali( in Africa started to disappear after catastrophic droughts in the 1970s). Over several years, droughts in the 1970s dried up the lake..
- The lake was once one of the largest in West Africa used to be fed by annual flooding from the Niger River.
- Then sand filled the channels connecting the lakes to the River Niger, with the result that when rain finally returned the water could no longer reach the lakes.
➡️UPSC 2023 General Studies Course: https://sleepyclasses.com/general-studies-for-upsc/
➡️Sociology Optional for UPSC : https://sleepyclasses.com/sociology-for-upsc/
➡️Political Science and IR for UPSC: https://sleepyclasses.com/psir-for-upsc/
➡️Signup here – https://sleepyclasses.com/
Have any query related to UPSC preparation: 📞Contact Us ► Toll-Free: 1800 890 3043 ► Mobile: 6280133177 ► Email: Sleepy.Classes@gmail.com ► WhatsApp: 6280133177



