About UN
- The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945.
- Currently made up of 193 Member States, the UN and its work are guided by the purposes and principles contained in its founding Charter.
- The UN has evolved over the years to keep pace with a rapidly changing world.
- But one thing has stayed the same: it remains the one place on Earth where all the world’s nations can gather together, discuss common problems, and find shared solutions that benefit all of humanity.


Emblem of UN
- With a pair of olive tree branches and a map of the world.
- The emblem and the flag on which it rests are also aspirational symbols for people all over the world, for they speak to their hopes and dreams of peace and unity
Secretary General of UN

- The Secretary-General is Chief Administrative Officer of the UN – and is also a symbol of the Organization’s ideals and an advocate for all the world’s peoples, especially the poor and vulnerable.
- The Secretary-General is appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a 5-year, renewable term.
- The current Secretary-General, and the 9th occupant of the post, is António Guterres of Portugal, who took office on 1 January 2017.
- On the 18th of June, 2021, Guterres was re-appointed to a second term, pledging as his priority to continue helping the world chart a course out of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Predecessor of UN
- The predecessor of the United Nations was the League of Nations, established in 1919, after World War I, under the Treaty of Versailles “to promote international cooperation and to achieve peace and security.“
- As of 20 April 1946, the League of Nations ceased to exist, having handed over all of its assets to the United Nations, and having granted the new UN Secretariat full control of its Library and archives.
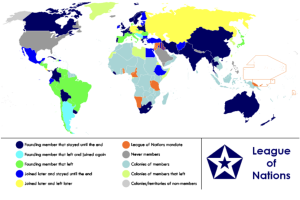

History of Foundation of UN

- The forerunner of the United Nations was the League of Nations, an organization conceived in circumstances of the First World War and established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles “to promote international cooperation and to achieve peace and security.
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) was also created in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles as an affiliated agency of the League.
- The name “United Nations”, coined by United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt.

United Nations Conference on International Organization (1945)
- The United Nations Conference on International Organization (UNCIO), commonly known as the San Francisco Conference.
- It was a convention of delegates from 50 Allied nations that took place from 25 April 1945 to 26 June 1945 in San Francisco, California, United States.
- Conference held in San Francisco (USA), was attended by representatives of 50 countries and signed the United Nations Charter.
- The UN Charter of 1945 is the foundational treaty of the United Nations, as an inter-governmental organization.
- 24 October 1945 (now observed annually as United Nations Day)
Founding Member States
- In accordance with Article 110, the Charter entered into force on 24 October 1945, after ratification by the five permanent members of the Security Council and a majority of the other countries.

NGST
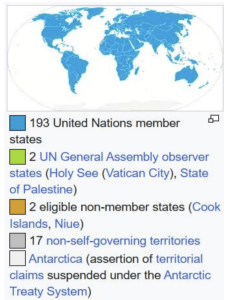
- Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter defines a non-self-governing territory (NSGT) as a territory “whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government”.
- In practice, an NSGT is a territory deemed by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) to be “non-self-governing”.
- Since 1946, the UNGA has maintained a list of non-self governing territories under member states’ control.
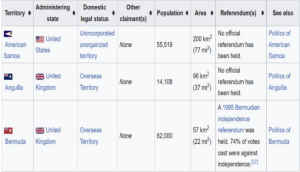
Some of the NGST –
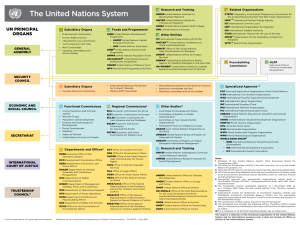
UN System

General Assembly
- The General Assembly is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the UN.
- All 193 Member States of the UN are represented in the General Assembly, making it the only UN body with universal representation.
- Each year, in September, the full UN membership meets in the General Assembly Hall in New York for the annual General Assembly session, and general debate, which many heads of state attend and address.
- Decisions on important questions, such as those on peace and security, admission of new members and budgetary matters, require a two-thirds majority of the General Assembly.
- Decisions on other questions are by simple majority.
- The General Assembly, each year, elects a GA President to serve a one-year term of office.
Security Council
- The Security Council has primary responsibility, under the UN Charter, for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- It has 15 Members (5 permanent and 10 non-permanent members).
- Each Member has one vote.
- Under the Charter, all Member States are obligated to comply with Council decisions.
- The Security Council takes the lead in determining the existence of a threat to the peace or act of aggression.
- It calls upon the parties to a dispute to settle it by peaceful means and recommends methods of adjustment or terms of settlement.
- In some cases, the Security Council can resort to imposing sanctions or even authorize the use of force to maintain or restore international peace and security.
- The Security Council has a Presidency, which rotates, and changes, every month.
India’s Track at UNSC

- As we know in January 2021, India joined the UNSC for its 8th term as a non-permanent member.
- India secured 184 votes in the 193-member General Assembly.
- Which includes all the 55 votes of the Asia-Pacific Group.
India as a Non-Permanent Member
- India was elected as a non-permanent member of the UNSC seven times.
- 1950–51, 1967–68, 1972–73, 1977–78, 1984–85, 1991–92, and 2011–12.
- Interestingly India’s UNSC membership always coincided with some significant events in international politics.
Presidency Amidst Chaos
- India’s first term in the Council and its first presidency coincided with the outbreak of the Korean War (1950–51).
- During India’s 2nd and 3rd terms there were heightened tensions in West Asia.
- Notably the two Arab–Israeli wars in 1967 and 1973.
Economic & Social Council
- The Economic and Social Council is the principal body for coordination, policy review, policy dialogue and recommendations on economic, social and environmental issues, as well as implementation of internationally agreed development goals.
- It serves as the central mechanism for activities of the UN system and its specialized agencies in the economic, social and environmental fields, supervising subsidiary and expert bodies.
- It has 54 Members, elected by the General Assembly for overlapping three-year terms.
- It is the United Nations’ central platform for reflection, debate, and innovative thinking on sustainable development.
Few Important Bodies Under the Purview of ECOSOC
- International labour Organization (ILO)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Bretton Woods Twins (World Bank Group and International Monetary Fund)
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
Trusteeship Council
- The Trusteeship Council, one of the main organs of the UN, was established to supervise the administration of trust territories as they transitioned from colonies to sovereign nations.
- The Council suspended its activities in 1994, when Palau, the last of the original 11 trust territories, gained its independence.
- The Trusteeship Council suspended operation on 1 November 1994.
- Although under the United Nations Charter it continues to exist on paper, its future role and even existence remains uncertain.
ICJ
- The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations.
- Its seat is at the Peace Palace in the Hague (Netherlands).
- It is the only one of the six principal organs of the United Nations not located in New York (United States of America).
- The Court’s role is to settle, in accordance with international law, legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies.
- The International Court of Justice functions in accordance with its Statute.
- The Court is composed of 15 judges, who are elected for terms of office of nine years by the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- It is assisted by a Registry, its administrative organ. Its official languages are English and French.
- The ICJ is the only international court that adjudicates general disputes between countries.
- With its rulings and opinions serving as primary sources of international law.
- All member states of the UN are party to the ICJ Statute and may initiate contentious cases.
- The International Court of Justice is composed of 15 judges elected to nine-year terms of office by the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- These organs vote simultaneously but separately.
- In order to be elected, a candidate must receive an absolute majority of the votes in both bodies.
- In order to ensure a degree of continuity, one third of the Court is elected every three years.
- Judges are eligible for re-election.
Secretariat
- The Secretariat comprises the Secretary-General and tens of thousands of international UN staff members who carry out the day-to-day work of the UN as mandated by the General Assembly and the Organization’s other principal bodies.
- The Secretary-General is Chief Administrative Officer of the Organization, appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a five-year, renewable term.
- The Secretary-General is also a symbol of the Organization’s ideals, and an advocate for all the world’s peoples, especially the poor and vulnerable.
➡️UPSC 2023 General Studies Course: https://sleepyclasses.com/general-studies-for-upsc/
➡️Sociology Optional for UPSC: https://sleepyclasses.com/sociology-for-upsc/
➡️Political Science and IR for UPSC: https://sleepyclasses.com/psir-for-upsc/
➡️Signup here – https://sleepyclasses.com/
Have any query related to UPSC preparation: 📞Contact Us ► Toll-Free: 1800 890 3043 ► Mobile: 6280133177 ► Email: Sleepy.Classes@gmail.com ► WhatsApp: 6280133177



