Question 1
Economy | Trade | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. India’s export promotion mission is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Commerce, Mirco, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and Finance.
2. Foreign Trade Policy 2023 provides the structure within which the Export Promotion Mission functions.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Both 1 and 2
Detailed Explanation
- India’s export promotion mission was announced in the 2025-26 Union Budget presented by the finance minister with a budget allocation of Rs 2,250 crore. This mission is a major step for India to make its global trade more competitive.
- India’s export promotion mission is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Commerce, Mirco, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and Finance. The ministries will set specific export targets for each sector and will take necessary steps for the same. Thus, helping India boost its presence in global markets.
- This initiative operates within India’s broader export facilitation system, which was built upon the foundation established by the Foreign Trade Policy 2023. Foreign Trade Policy 2023 has four key pillars: Incentive to remission, Export promotion through collaboration, Ease of doing business and Emerging areas. This framework provides the structure within which the Export Promotion Mission functions.
Question 2
Polity | Scheduled Tribe | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. Forest Rights contain individual rights only.
2. The Gram Sabha enjoys more power under FRA, 2006 as compared to other gram sabhas in non-ST areas.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) 2 only
Detailed Explanation
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006 recognizes the rights of the forest dwelling tribal communities and other traditional forest dwellers to forest resources, on which these communities were dependent for a variety of needs, including livelihood, habitation and other socio-cultural needs. The forest management policies, including the Acts, Rules and Forest Policies of Participatory Forest Management policies in both colonial and post-colonial India, did not, till the enactment of this Act, recognize the symbiotic relationship of the STs with the forests, reflected in their dependence on the forest as well as in their traditional wisdom regarding conservation of the forests.
- The Act encompasses Rights of Self-cultivation and Habitation which are usually regarded as Individual rights; and Community Rights as Grazing, Fishing and access to Water bodies in forests, Habitat Rights for PVTGs, Traditional Seasonal Resource access of Nomadic and Pastoral community, access to biodiversity, community right to intellectual property and traditional knowledge, recognition of traditional customary rights and right to protect, regenerate or conserve or manage any community forest resource for sustainable use. It also provides rights to allocation of forest land for developmental purposes to fulfil basic infrastructural needs of the community. In conjunction with the Right to Fair Compensation and Transparency in Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Settlement Act, 2013 FRA protects the tribal population from eviction without rehabilitation and settlement.
- The Act further enjoins upon the Gram Sabha and rights holders the responsibility of conservation and protection of bio-diversity, wildlife, forests, adjoining catchment areas, water sources and other ecologically sensitive areas as well as to stop any destructive practices affecting these resources or cultural and natural heritage of the tribals. The Gram Sabha is also a highly empowered body under the Act, enabling the tribal population to have a decisive say in the determination of local policies and schemes impacting them.
- Thus, the Act empowers the forest dwellers to access and use the forest resources in the manner that they were traditionally accustomed, to protect, conserve and manage forests, protect forest dwellers from unlawful evictions and also provides for basic development facilities for the community of forest dwellers to access facilities of education, health, nutrition, infrastructure etc.
- Objectives
- To undo the historical injustice occurred to the forest dwelling communities
- To ensure land tenure, livelihood and food security of the forest dwelling Scheduled Tribes and other traditional forest dwellers
- To strengthen the conservation regime of the forests by including the responsibilities and authority of Forest Rights holders for sustainable use, conservation of biodiversity and maintenance of ecological balance.
Question 3
Science and Technology | Space | Medium | the Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following with respect to Pixxel-Space and INSPACE Project:
1. It is a cluster of 20 earth observation satellites.
2. The constellation will feature hyperspectral satellites.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) 2 only
Detailed Explanation
- In a historic first for the country, a private Indian consortium will deliver the nation’s first Earth Observation Satellite System (EOSS) — a 12-satellite network to be developed over the next four to five years with an investment of more than ₹1,200 crores. The project will enhance India’s data sovereignty, reduce dependence on foreign imagery, and ensure that all satellites are manufactured domestically, launched on Indian rockets, and controlled from within the country.
- The constellation will feature a mix of sub-metre very high-resolution, wide-swath multispectral, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), and hyperspectral satellites, enabling applications such as precision agriculture, water quality monitoring, land-use mapping, environmental compliance, disaster assessment, and infrastructure development.
Question 4
International Relations | South China Sea | Easy | the Hindu
SOURCE
Which of the following countries does not border South China sea?
A. Malaysia
B. Brunei
C. Indonesia
D. Japan
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) Japan
Detailed Explanation
- The South China Sea is bordered by China, Taiwan, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, and Vietnam. It is a strategically important area connecting the Indian and Pacific Oceans and also holds significant biodiversity, fisheries, and potential oil and gas reserves.
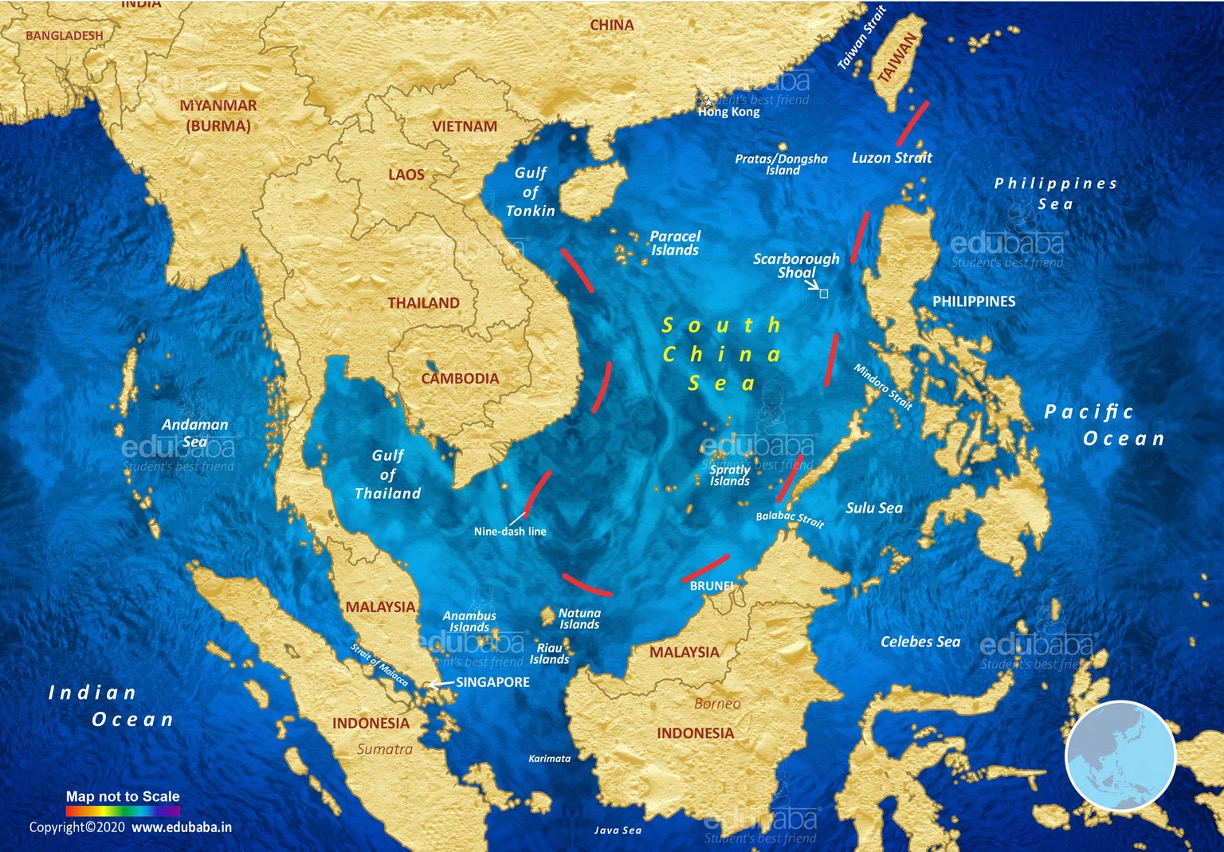
Question 5
International Relations | E3 | Hard | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following statements:
1. The E3 originated in 2003.
2. These three countries are the most politically and economically influential EU member states, with the largest populations.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Both 1 and 2
Detailed Explanation
- The EU three, also known as the EU big three, EU triumvirate, EU trio or simply E3, refers to France, Germany, and Britain, the three large founding members of the European Union (EU). These countries are generally regarded as the three most politically and economically influential EU member states, with the largest populations, highest military expenditures, and largest economies by nominal GDP, collectively accounting for over half of the EU’s economic output.
- Before Brexit, the term was also used to refer to the grouping of France, Germany, and the United Kingdom, especially during the negotiations with Iran from 2003.
- In 2003, France, Germany and the UK launched negotiations attempting to limit the Iranian nuclear program, which led to the Tehran Declaration of 21 October 2003 and the voluntary Paris Agreement of 15 November 2004 wherein Iran agreed to temporarily suspend all uranium enrichment and reprocessing activities, including those related to centrifuges.
- EU 3 + 3, more commonly referred to as the E3+3, refers to a grouping which includes the EU-3 and China, Russia, and the United States. It was coined when these states joined the EU diplomatic efforts with Iran in 2006. In the United States and Russia, it is more commonly known as P5+1, which refers to the five permanent members of the UN Security Council plus Germany.
Question 6
Governance | Education | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. The pre and post matric scholarship program for SC and ST students is a Centrally Sectored Scheme.
2. The parental income currently required for pre and post matric scholarship is Rs 2. 5 lakh annually.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) 2 only
Detailed Explanation
- These scholarships require eligible candidates to have parental annual income below 22. 5 lakh. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs is looking to raise parental income limit to 74. 5 lakh for post and pre-matric ST scholarships, and the Social Justice Ministry is discussing revising the limits for post and pre-matric scholarships for Scheduled Castes (SCs), Other Backward Castes (OBCs), and De-notified Tribes (DNTs). In addition, discussions are also on to raise the parental income limit of college and school scholarships for OBCs, and DNTs.
- The post and pre-matric scholarships for SCs, Scheduled Tribes (STs), and OBCs, are run as central sponsored schemes by the government. This means that it is funded by both the Union and State governments on a 60:40 ratio (Union:States), except for in northeast States where the ratio is 90:10.
Question 7
Polity | Reservation | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. The 104th Constitutional Amendment Act extended the reservation of seats for SC and ST till 2030.
2. Mandal Commission case, established the 50% ceiling limit for reservations in India.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Both 1 and 2
Detailed Explanation
- The 104th Constitutional Amendment Act, passed in 2020, primarily focused on extending the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies for another ten years, while simultaneously discontinuing the reservation for the Anglo-Indian community in these bodies.
- Extension of SC/ST Reservations: The amendment extended the existing reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies for an additional 10 years, ensuring these provisions until 2030.
- Abolition of Anglo-Indian Representation: The 104th Amendment discontinued the practice of nominating members of the Anglo-Indian community to the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies.
- Historical Context: The original reservation for SCs and STs was introduced in the Constitution in 1950 for a period of 70 years. The 104th Amendment ensured these reservations continue for another decade, while ending the special provision for the Anglo-Indian community.
- Purpose: The amendment aimed to ensure continued political representation for marginalized communities (SCs and STs) and to address the perceived need for their continued inclusion in the political process.
- The Indra Sawhney case, also known as the Mandal Commission case, established a 50% ceiling limit for reservations in India. This landmark judgment, delivered by the Supreme Court, upheld the 27% reservation for Other Backward Classes (OBCs) recommended by the Mandal Commission while also imposing a cap on the total reservation quota. The court’s decision aimed to balance affirmative action with the principles of equality and merit.
- Mandal Commission: The Mandal Commission was appointed in 1979 to identify socially and educationally backward classes and recommend measures for their upliftment.
- Key Recommendations:
- The commission’s report, submitted in 1980, proposed a 27% reservation in government jobs for OBCs, who were identified based on specific criteria.
- Indra Sawhney Case: In 1992, the Supreme Court heard a case challenging the implementation of the Mandal Commission’s recommendations. The case, formally known as Indra Sawhney & Ors. v. Union of India & Ors., addressed various aspects of reservation policy.
- 50% Ceiling: The Supreme Court, in its judgment, upheld the 27% reservation for OBCs but also established that the total reservation (including existing reservations for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) should not exceed 50%.
- Creamy Layer: The court also introduced the concept of the “creamy layer,” which refers to the socially advanced members of the backward classes who are excluded from reservation benefits, ensuring that the benefits reach the truly deserving.
- Impact: The Indra Sawhney judgment has had a lasting impact on India’s reservation policy, shaping the framework for affirmative action and influencing subsequent legal and policy decisions.




