Question 1
Geography | Places In News | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. Palk Bay is one of the major sinks for sediments along with the Gulf of Mannar.
2. Palk Strait connects the Palk Bay in the Bay of Bengal with the Laccadive Sea.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Both 1 and 2
Detailed Explanation
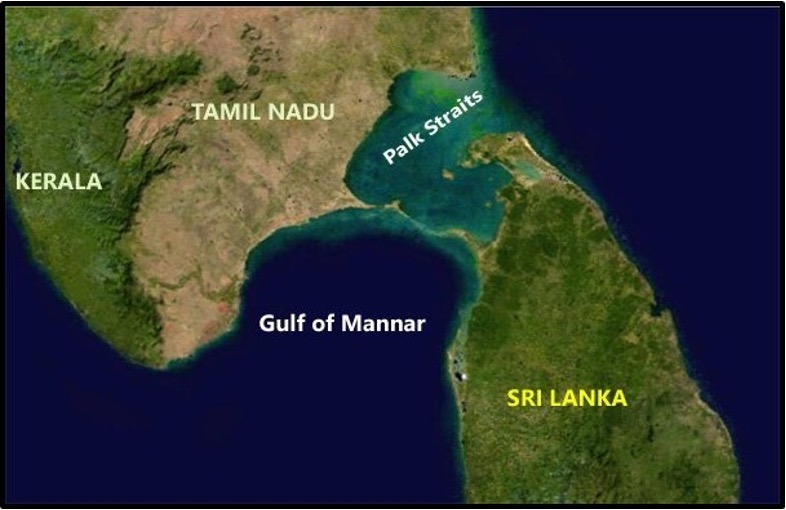
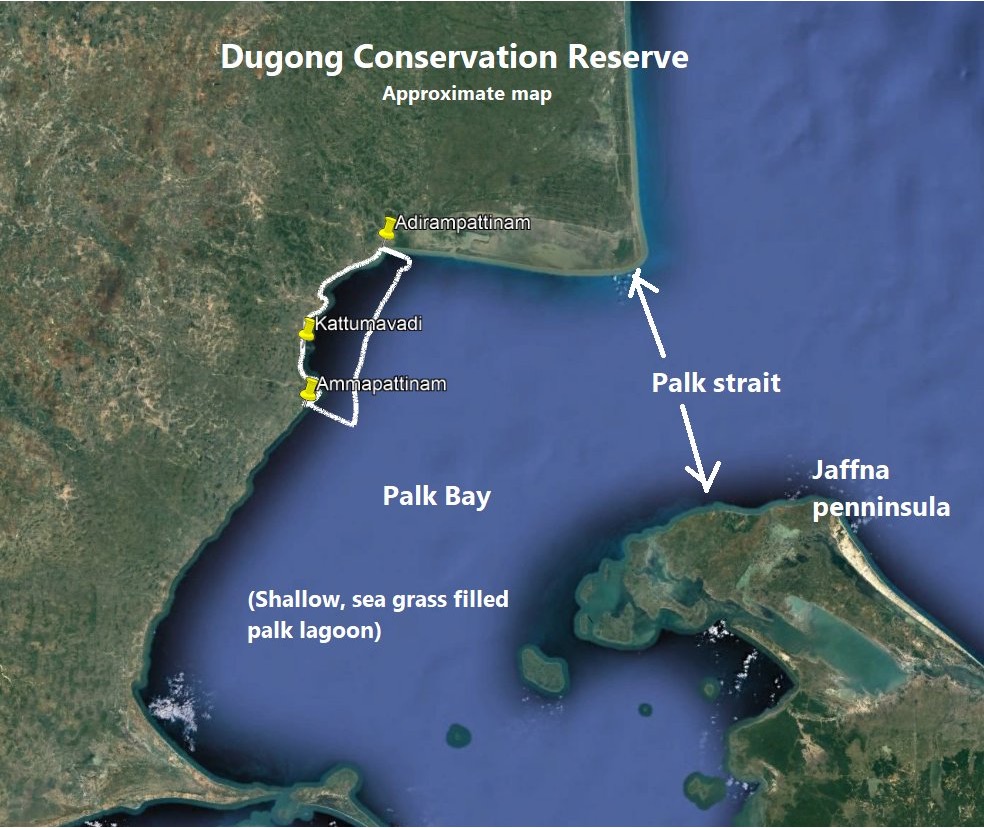
- Palk Bay is a semi-enclosed shallow water body between the southeast coast of India and Sri Lanka, with a water depth maximum of 13 m.Palk Bay is located between 8° 50′ and 10° North latitudes and 78° 50′ and 80° 30′ East longitudes. The width of the bay ranges from 57 to 107 km and the length is around 150 km. It is one of the major sinks for sediments along with the Gulf of Mannar. Sediments discharged by rivers and transported by the surf currents as littoral drift settle in this sink.
- Palk Strait is a strait between the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It connects the Palk Bay in the Bay of Bengal in the north with the Gulf of Mannar in the Laccadive Sea in the south. It stretches for about 137 km (85 mi) and is 64 to 137 km (40 to 85 mi) wide.
Question 2
Science And Technology | Defence | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. SAKSHAM will provide airspace security across the Air Littoral upto10,000 metres.
2. SAKSHAM is a high-end Command, Control and Communication (C3) system.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
- Indian Army has initiated procurement of the indigenously developed ‘Saksham’ Counter-Unmanned Aerial System (CUAS) Grid System. The system is designed to detect, track, identify, and neutralise hostile drones and unmanned aerial systems in real time, ensuring comprehensive airspace security across the newly defined Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS), which now includes the Air Littoral (airspace up to 3,000 metres, or 10,000 feet, above ground level).
- Developed in collaboration with the Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Ghaziabad, Saksham, or Situational Awareness for Kinetic Soft and Hard Kill Assets Management, is a modular, high-end Command and Control (C2) system operating on the secure Army Data Network (ADN). It creates a real-time, integrated Recognised UAS Picture (RUASP) for commanders, merging sensor data, counter-drone systems, and AI-driven analytics.
- The system will have features like real-time threat detection and AI-enabled predictive analysis, integration of CUAS sensors and weapons for synchronised response, automated decision support and 3D battlefield visualisation, seamless interoperability with other operational systems, and inputs from the Akashteer System to map all friendly, neutral, and hostile airspace users.
- Saksham reflects the government’s vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat in defence technology and is completely indigenous. Approved under the Fast Track Procurement (FTP) route, it will be rolled out to all field formations within a year.
- The initiative marks a decisive stride toward a digitally enabled, networked battlefield, aligned with the Army’s Decade of Transformation (2023–2032).
Question 3
Governance | Schemes | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following in context of Pulse Self-Reliance Mission:
1. The aim is to expand the total pulse cultivation area to 31 million hectares by 2030-31.
2. Productivity is targeted to increase from 880 kg per hectare to 1,500 kg per hectare.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- India is both the largest producer and consumer of pulses, it continues to be the biggest importer.
- Hence, the government has launched the Pulse Self-Reliance Mission to boost production, productivity, and cultivated area.
- The aim is to expand the total pulse cultivation area from 27. 5 million hectares to 31 million hectares by 2030-31, and to raise production from 24. 2 million tonnes to 35 million tonnes.
- Productivity is targeted to increase from 880 kg per hectare to 1,130 kg per hectare.


Question 4
Social Issues | Important Issues | Hard | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, permits only altruistic surrogacy.
2. Commercial surrogacy is punishable with a jail term of 10 years or a fine of up to Rs 10 lakhs.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- India’s surrogacy laws, established by the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, permit only altruistic surrogacy for Indian married heterosexual couples and OCI cardholders with proven infertility, while prohibiting commercial surrogacy and excluding single parents and LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Eligibility criteria apply to both the intending couple and the surrogate, who must be a married Indian woman between 25-35, have a child of her own, and undergo mandatory medical and psychological screenings.
- The law requires clinics to be registered, bans surrogate advertising, mandates insurance for the surrogate for 36 months, and establishes a District Medical Board for approvals.
- Altruistic Surrogacy Only: Only altruistic surrogacy, where the surrogate receives no monetary compensation beyond medical expenses and insurance, is legal in India.
- Commercial Surrogacy Banned: Commercial surrogacy, involving monetary profit beyond basic medical costs, is illegal and punishable by law.
- Intending Couple Eligibility: Must be an Indian married, heterosexual couple, including OCI cardholders. Must be married for at least five years. Must have a certificate of essentiality and eligibility from an appropriate authority. Must suffer from proven infertility, certified by a District Medical Board.
- Surrogate Mother Eligibility: Must be an Indian woman. Must be a married woman with a biological child of her own.
- Age range: 25-35 years. Must undergo mandatory medical and psychological screening. Can act as a surrogate only once in her lifetime.
- Regulatory Bodies
- District Medical Board: Approves applications for surrogacy, certifying the medical necessity for the intending couple
- National Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Registry: A registry for all surrogacy clinics and services.
- Clinic and Advertising Regulations: All clinics offering surrogacy services must be registered with the government. Advertising for recruiting surrogate mothers is prohibited.
- Insurance and Child’s Rights: The surrogate must have medical insurance for 36 months after delivery. The child born through surrogacy is legally recognized as the child of the intending parents.
- Gamete Donation: The use of donor gametes (eggs or sperm) is allowed if a District Medical Board certifies a medical necessity. There are regulations on who can donate gametes, including an age limit and a restriction on donating oocytes only once in a lifetime.
- Exclusions from Surrogacy
- Single parents, foreigners, and LGBTQ+ couples are ineligible to opt for surrogacy.
- Live-in couples are also excluded from the current framework, despite court recognition of such relationships.
Question 5
Environment | Conservation | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is a multilateral treaty adopted at the Earth Summit in 1992.
2. The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) is a UN agreement adopted in 2017.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is a multilateral treaty adopted at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, with the main goals of conserving biodiversity, using it sustainably, and fairly sharing the benefits from genetic resources. Coming into force on December 29, 1993, it is a legally binding international agreement under the United Nations Environment Programme, with 196 countries as Parties. The CBD is a key document for sustainable development, recognizing that biodiversity is essential for people’s well-being and the environment.
- Aspect:
- Objectives: The CBD has three main objectives:
- Conservation of biological diversity.
- Sustainable use of the components of biological diversity.
- Fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources.
- Origin: The convention was negotiated and signed at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
- Entry into Force: It became legally binding on December 29, 1993.
- International Legal Instrument: The CBD serves as the international legal framework for biodiversity conservation.
- Governing Body: The Conference of the Parties (COP) is the governing body of the convention, made up of the governments that have ratified the treaty.
- Secretariat: The Secretariat of the CBD is located in Montreal, Canada.
- Global Participation: 196 countries are parties to the convention, including India, which ratified it in 1994.
- Why it Matters
- Sustainable Development: The CBD is a central document in the global effort to achieve sustainable development.
- Practical Tool: It functions as a practical tool for translating the principles of sustainable development into action.
- Human Well-being: The convention acknowledges that biodiversity is vital for human needs, including food security, medicines, clean air and water, and a healthy environment.
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) is a UN agreement adopted in 2022 at the 15th Conference of the Parties (COP15) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- It sets a 2050 Vision for living in harmony with nature, supported by 2050 Goals and 23 actionable targets for 2030.
- The framework emphasizes ecosystem restoration, sustainable management of natural resources, and the fair sharing of benefits from genetic resources.
- Key Components:
- 2050 Vision: A future where people live in harmony with nature.2050 Goals: Four overarching goals to achieve the 2050 vision 2030 Targets: 23 specific, measurable targets for action by 2030 to put nature on the path of recovery.
- Main Objectives:
- Halt and reverse biodiversity loss: To achieve a healthier planet with recovering ecosystems by 2030. Sustainable use of components: To promote the sustainable use of biodiversity for the long-term benefit of all. Benefit sharing: To ensure that the benefits from the use of genetic resources are shared fairly and equitably.
- Adoption and Implementation:
- The framework was agreed upon by parties to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity at COP15 in Kunming, China, and finalized in Montreal, Canada, in December 2022.
- Countries are expected to align their national biodiversity strategies and action plans (NBSAPs) with the GBF’s targets and goals.
- A monitoring framework is established to track progress, with reviews at each subsequent COP meeting.
- Significance:
- Often called the “Paris Agreement for Nature,” the GBF provides a global roadmap for conservation and sustainable use of nature.
- It calls for urgent and transformative action across governments, businesses, and civil society to address the drivers of nature loss.
Question 6
Economy | Market | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. The Securities and Exchange Board of India was constituted as a non-statutory body.
2. The provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act came into force in 1988.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India was constituted as a non-statutory body on April 12, 1988 through a resolution of the Government of India.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India was established as a statutory body in the year 1992 and the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (15 of 1992) came into force on January 30, 1992.
Question 7
International Relations | Maritime Exercise | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. ReSAREX is a biannual exercise.
2. Vayam Rakshamah is the motto of the Indian Coast Guard.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) 2 only
Detailed Explanation
- ReSAREX stands for Regional Search and Rescue Exercise, and it is an annual maritime exercise conducted by the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) to test and improve its coordination and preparedness in handling mass rescue operations at sea. The most recent exercise, ReSAREX–25, was successfully held off the coast of Karnataka to evaluate the ICG’s operational readiness and inter-agency communication, reinforcing its commitment to safeguarding lives and property.
- The Indian Coast Guard’s motto is ” Vayam Rakshamah” which translates to “We Protect” in English. This Sanskrit phrase is inscribed on the Coast Guard’s scroll and reflects its commitment to safeguarding India’s maritime interests and resources.
Question 8
Current Affairs | Nobel Prize | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following pairs: (Years and Nobel Prize in Literature)
2024 – Jon Fosse
2023 – Annie Ernaux
2022 – Han Kang
How many pairs is or are correctly matched?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation









