Question 1
Geography | International Borders | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following pairs: (Land Borders and The Countries)
Hindenburg Line – Russia and Finland
Mannerheim Line – Israel and Lebanon
Blue Line – Germany and Poland
How many pairs is or are correctly matched?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
- The border demarcation published by the United Nations on June 7, 2000, is known as the Blue Line. It was created to determine the extent of Israel’s withdrawal from southern Lebanon and is based on a 1923 boundary agreement, although the UN itself stated it is a withdrawal line and not an official international border. The Blue Line stretches for roughly 120 km from the Mediterranean Sea to north of the Golan Heights and is marked by 272 blue barrels.
- The term “Hindenburg line” refers to a German defensive fortification on the Western Front during World War I, stretching from Arras toLaffaux in northeastern France, but it can also refer to the Oder-Neisse line, which is the border between Germany and Poland established after World War II. The WWI defensive line was an extensive system of trenches and concrete pillboxes built in 1917, which was ultimately breached by Allied forces in 1918. The Oder-Neisse line, sometimes called the Hindenburg Line in some contexts, is the current border between Germany and Poland, named after the Oder and Neisse rivers.
- The Mannerheim Line was a defensive fortification line built by Finland across the Karelian Isthmus to guard against the Soviet Union. Named after Baron von Mannerheim, it was constructed in two main phases, 1920–1924 and 1932–1939, to protect against a potential Soviet invasion, which occurred during the Winter War of 1939-1940. The line, though not fully finished and partially outdated when the war began, was a crucial and effective defensive system that slowed the Soviet advance and inflicted heavy casualties
Question 2
Economy | Industries | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Arrange the following core industries from lowest to highest as per their weightage in the IIP:
1. Crude Oil
2. Cement
3. Electricity
4. Petrol
5. Natural Gas
A. 2,5,1,3,4
B. 2,1,3,5,4
C. 2,3,1,5,4
D. 2,3,5,1,4
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 2,5,1,3,4
Detailed Explanation

Question 3
International Relations |International Organisations | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. Most plenaries are held in Paris at the OECD conference facilities.
2. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) holds two main plenary meetings each year.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) holds three main plenary meetings each year, typically in October, February, and June, to discuss and make decisions on combating money laundering and terrorist financing. These meetings are not open to the public and are attended by delegations from member and observer countries.
- Many plenary sessions for international bodies are held in Paris at the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) conference facilities. This statement is particularly true for meetings of the OECD’s own networks and committees, as well as for organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), which has a close relationship with the OECD.
- Examples of plenaries held at OECD facilities in Paris
- OECD Global Parliamentary Network (GPN): The annual plenary meeting for this network of parliamentarians regularly takes place at the OECD Conference Centre in Paris.
- OECD Ministerial Council Meeting (MCM): This major annual meeting of OECD ministers is held at the organization’s headquarters in Paris.
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): This intergovernmental body dedicated to combating money laundering and terrorist financing often holds its plenary sessions at the OECD conference facilities.
- Global Forum on Tax Transparency and Exchange of Information for Tax Purposes: This body, which operates under the OECD, holds its annual plenary meeting in Paris.
Question 4
Polity | Terms | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. The de jure head of India is the Prime Minister.
2. The de facto head of India is the President.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
- The de jure head of India is the President of India, who is the nominal head of state and holds the highest office legally. The President is the constitutional head, while the Prime Minister is the de facto or real head of government, who exercises the actual executive powers.
- De jure head: The President is the head of state as defined by law, holding formal power and acting as the first citizen. The current President is Droupadi Murmu.
- De facto head: The Prime Minister is the head of government and holds the real executive authority, leading the Council of Ministers.
- Reasoning: In India’s parliamentary system, the President is the nominal executive (de jure), while the Prime Minister is the real executive (de facto).
Question 5
Environment | Pollution | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. Very high wind speeds disperse pollutants lowering PM levels.
2. Low wind speeds allow PM to accumulate leading to higher concentrations.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) 2 only
Detailed Explanation
- Wind speed has a complex relationship with particulate matter (PM) concentrations: generally, higher wind speeds disperse pollutants, lowering PM levels, but very high winds can increase PM by resuspending particles from the ground. Low wind speeds allow PM to accumulate, leading to higher concentrations, especially fine particles like PM2. 5 from local sources. The effect is not uniform, as high winds can move coarse particles like dust more effectively, and wind direction can transport pollutants from a different source region.
- Low wind speed: Pollutants and fine particles (like PM2. 5) are not dispersed effectively and can accumulate, leading to higher concentrations.
- Moderate wind speed: Typically results in lower PM concentrations as pollutants are dispersed and transported away from the area.
- High wind speed: Can cause a rapid increase in PM, especially PM10, because the strong winds lift and resuspend particles already on the surface (like dust).
Question 6
Economy | Trade | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
If the supply of final goods is assumed to be infinitely elastic at constant price over a short period of time, Aggregate output is determined solely by the value of Aggregate demand. This is called __________ Principle.
A. Aggregate supply
B. Aggregate demand
C. Effective demand
D. Perfectly inelastic demand
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Effective demand
Detailed Explanation
- Aggregate supply: Aggregate supply is the total amount of goods (including services) supplied by businesses within a country at a given price level. The higher the price level, the greater the incentive of businesses to produce more of their goods for the market.
- Aggregate demand: Aggregate demand is a term used in macroeconomics to describe the total demand for goods produced domestically, including consumer goods, services, and capital goods. It adds up everything purchased by households, firms, government and foreign buyers (via exports), minus that part of demand that is satisfied by foreign producers through imports. This is often written as C + I + G + (X-M), where C is personal consumption expenditures, I is investment, G is government purchases of goods and services, X is exports, and M is imports. Together, this is all of Gross Domestic Product, or GDP.
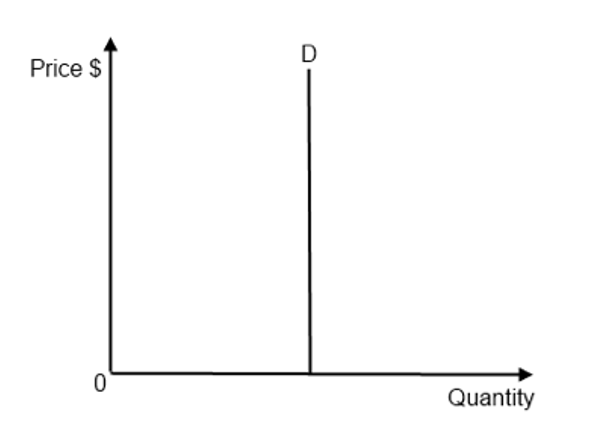
- Effective demand: The supply of final goods is assumed to be infinitely elastic at constant price over a short period of time, Aggregate output is determined solely by the value of Aggregate demand.
- Perfectly inelastic demand curve: It states that the quantity demand will remain the same irrespective of the change in prices. The consumer will demand the same quantity of commodities even if the price is high or low. Price elasticity here will be zero.
Question 7
International Relations | International Treaties | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. The Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances was signed in 1994.
2. In exchange for Ukraine giving up its inherited nuclear weapons, the other signatories provided security assurances to respect Ukraine’s independence.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Both 1 and 2
Detailed Explanation
- The Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances was signed in Budapest on December 5, 1994, by Ukraine, Russia, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
- In exchange for Ukraine giving up its inherited nuclear weapons, the other signatories provided security assurances to respect Ukraine’s independence, sovereignty, and existing borders, and to refrain from the threat or use of force against it.
- Identical memorandums were also signed for Belarus and Kazakhstan in connection with their accession to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT).







