Question 1
Geography | Agriculture | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Which of the following are the conditions required for tea plantations:
1. Tropical-Subtropical Climate
2. Low humidity
3. Seasonal Rainfall
Choose the correct answer:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 only
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- Tea requires a tropical or subtropical climate with moderate temperatures (13-32°C), high humidity (around 80%), and frequent, well-distributed rainfall (150-250 cm annually). The ideal conditions are a moderately hot and humid environment, without prolonged frost, ensuring well-drained acidic soil is also present.
- Temperature: Tea plants thrive in moderate temperatures, generally between 13°C and 32°C. Temperatures above 32°C can be detrimental to the plant’s photosynthesis and growth, while frost is also harmful.
- Rainfall: A significant amount of rainfall, ideally between 150 cm and 250 cm, is needed annually. This rainfall should be consistent and well-distributed throughout the year to maintain soil moisture.
- Humidity: High levels of humidity are crucial for healthy growth, as they help maintain the necessary moisture in the soil and for the leaves.
- Altitude: While not strictly a climatic condition, higher altitudes (600-2,100 meters) often lead to superior tea quality due to cooler temperatures and increased cloud cover
Question 2
Environment | Climate Change | Hard | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
1. JCM is a framework for climate cooperation under Article 6. 2 of the Paris Agreement.
2. JCM focuses on reduction of carbon footprint in the Industrial sector only.
Which of the statements above is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
- The India-Japan Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) is a bilateral framework for climate cooperation under Article 6. 2 of the Paris Agreement, enabling both countries to collaborate on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and meet climate targets. Under the JCM, Japan supports India’s development of low-carbon technologies and projects, with resulting emission reductions shared between the two nations. This mechanism facilitates carbon trading, promotes green investment, and fosters technology transfer, with a joint committee overseeing its implementation.
- Key Aspects of the JCM
- Bilateral Framework: The JCM is a cooperative framework between India and Japan, allowing them to work together on climate action and contribute to global climate goals.
- Paris Agreement Alignment: It operates under Article 6. 2 of the Paris Agreement, which provides a framework for international carbon markets and cooperative approaches.
- Shared Credits: Emission reductions achieved through JCM projects are credited to both countries. Japan uses its credits to meet its own climate goals (Nationally Determined Contributions – NDCs), while India also benefits from the sustainable development promoted by the mechanism.
- Joint Committee: A joint committee is responsible for managing the JCM, including establishing rules, methodologies for projects, and handling the registration and sharing of credits.
- Investment in Low-Carbon Technologies: Japan provides financial and technological support to implement leading low-carbon technologies and measures in India.
- Host Country Involvement: Unlike some previous mechanisms, India participates as a joint implementer, having a significant role in the decision-making process.
- Benefits for India: The JCM offers India a way to attract green investment, develop its clean energy and manufacturing sectors, and adopt advanced emission-reducing technologies in various industries.
- Sectors Covered: The agreement is set to cover a range of sectors, including renewable energy with storage, green hydrogen production, sustainable aviation fuel, and the decarbonization of hard-to-abate industries.
Question 3
Environment | Conservation | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Mangroves are called the first line of defence because of:
1. Wave Energy Absorption
2. Stabilization of Shorelines
3. Increase of Surge Height and Water Velocity
Choose the correct answer:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. All of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 and 2 only
Detailed Explanation
- Mangroves serve as the first line of defense because their dense, tangled root systems absorb and disperse the energy of waves and storm surges, acting as natural barriers that protect coastal communities by reducing flooding, slowing erosion, and dissipating the force of tsunamis and hurricanes. This natural protective function is crucial for stabilizing shorelines, preventing soil loss, and mitigating the devastating impacts of extreme weather events on coastal infrastructure and habitats.
- Wave Energy Absorption: The intricate and dense root systems of mangroves act like a natural sponge, absorbing and breaking up the energy of incoming waves and storm surges before they reach the shore.
- Reduction of Surge Height and Water Velocity: By obstructing the flow of water, mangroves significantly reduce the height of storm surges and slow down the speed of water, minimizing flooding and damage to coastal areas.
- Erosion Control: Mangrove roots bind the soil together, preventing erosion and stabilizing the coastline against powerful wave action and strong currents.
- Stabilization of Shorelines: Their ability to trap sediments and build up soil helps maintain the integrity of coastal land and prevents the land from being washed away.
- Protection Against Extreme Weather: Mangroves provide crucial protection against natural hazards such as hurricanes, typhoons, and tsunamis by reducing the destructive forces they exert on coastlines.
- A Natural Barrier: Their physical structure and location at the transition between land and sea make them a powerful, natural buffer that shields coastal communities from the full impact of rising tides and violent storms.
Question 4
International Relations | Military Exercises | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following pairs: (Military Exercises and Countries)
Exercise Ekuverin – India and Bangladesh
Bano Sagar Naval Exercise – India and Russia
INDRA 2025 Naval Exercise – India and Maldives
How many pairs is or are correctly matched?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
- Exercise Ekuverin – India and Maldives
- Bano Sagar Naval Exercise – India and Bangladesh
- INDRA 2025 Naval Exercise – India and Russia
Question 5
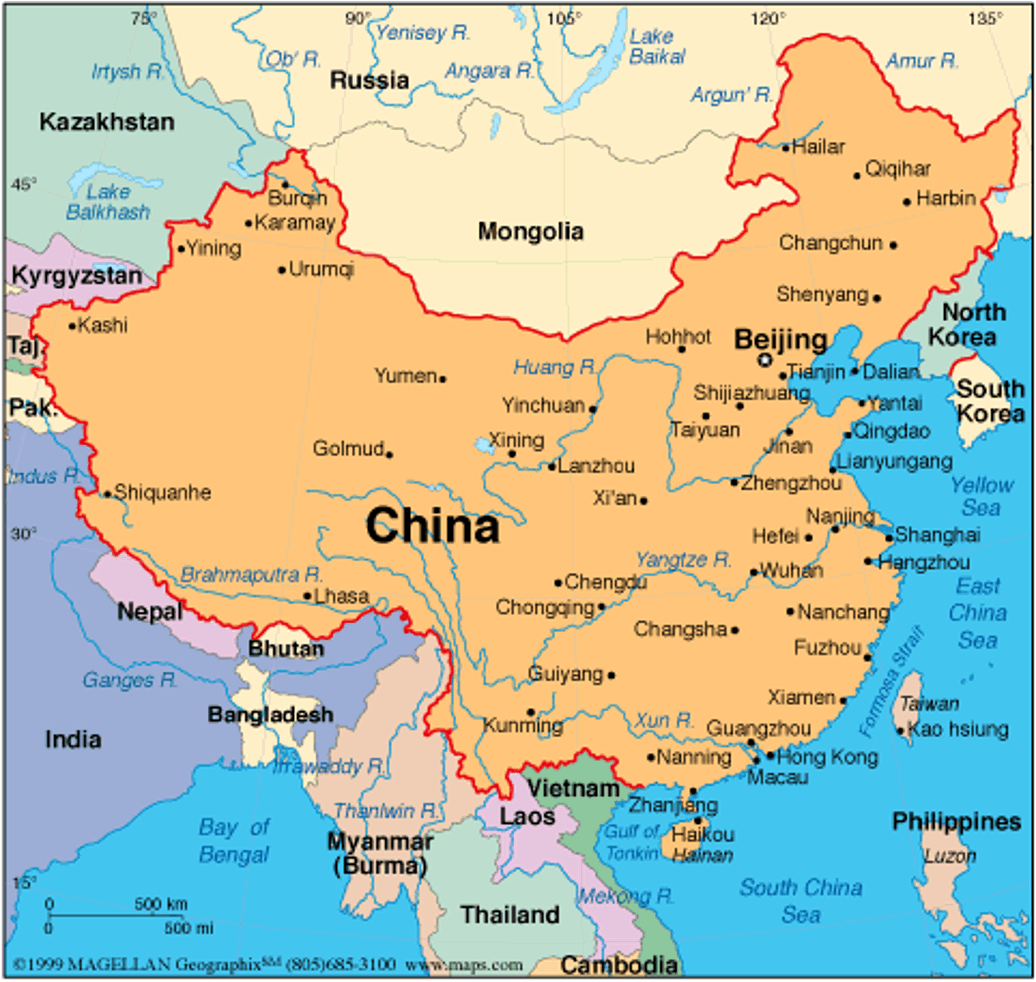
Geography | Maps | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Which among the following countries does not border China?
A. Laos
B. Uzbekistan
C. Tajikistan
D. Kazakhstan
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) Uzbekistan
Detailed Explanation
- China shares land borders with 14 countries: Afghanistan, Bhutan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Vietnam. It also has maritime borders with several countries in the South China Sea and Yellow Sea, including Japan, South Korea, the Philippines, and Taiwan.