Question 1
International Relations | International Treaties | Easy | Live Mint
SOURCE
Consider the following:
- Abraham Accords led to the formation of the West Asia Quad.
- Morocco was the first Arab country to agree on the Abraham Accords.
Which of the following statement is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (A) 1 only
Detailed Explanation
I2U2 is a strategic and economic grouping that includes India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States. It’s sometimes referred to as the “West Asian Quad” or “Middle East Quad”. The initiative focuses on joint investments and collaboration in areas like water, energy, transportation, space, health, and food security. Statement 1 is correct.
• About:
• The Abraham Accords are a series of agreements signed in 2020 between Israel and several Arab states, marking a historic shift in diplomatic relations in the Middle East.
• The Accords were named ‘Abraham Accords’ in reference to the supposed common ancestor of the Jews and the Arabs, the biblical Abraham, and as an expression of brotherhood.
• The primary countries involved in the Abraham Accords include:
• Israel: As a key party to the Accords, Israel agreed to normalize diplomatic relations with the participating Arab nations, marking a significant departure from the historically hostile relationships it had with many Arab states.
• United Arab Emirates (UAE): The UAE was the first Arab country to formally announce its normalization of relations with Israel under the Abraham Accords. This historic agreement includes the establishment of full diplomatic relations, as well as economic, technological, and cultural exchanges. Statement 2 is incorrect.
• Bahrain: Bahrain followed the UAE’s lead by signing a similar agreement with Israel. The Bahrain-Israel Peace Agreement also encompasses diplomatic relations and cooperation in various sectors.
• Sudan: Sudan joined the Abraham Accords by agreeing to normalize relations with Israel. This marked a major shift in Sudan’s foreign policy and led to the removal of Sudan from the U.S. list of state sponsors of terrorism.
• Morocco: Morocco, another Arab nation, joined the Accords with a commitment to normalize relations with Israel. This agreement included the United States’ recognition of Morocco’s sovereignty over Western Sahara in exchange for Morocco’s engagement with Israel.
Question 2
Miscellaneous | Acts | Hard | Live Mint
SOURCE
With reference to Customs and Tariffs Act 1975 , consider the following:
- The First Schedule of the Act deals with Export Tariff.
- Only the Central Government has the power to amend the first schedule.
Which of the following statement is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) 2 only
Detailed Explanation

Question 3
International Relations | Exercise | Easy | Live Mint
SOURCE
Consider the following pairs Evacuation programmes and Country:
Operation Devi Shakti – Ukraine
Operation Ganga – Haiti
Operation Indravati – Afghanistan
How many pairs are correctly matched?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
• Operation Devi Shakti: A total of 669 individuals have been evacuated from Afghanistan under “Operation Devi Shakti” by 6 IAF and Air India flights. This comprises 448 Indians and 206 Afghans, which includes members of the Afghan Hindu/Sikh community and 15 foreign nationals. Statement 1 is incorrect.
• Operation Ganga: 18,282 Indian nationals, mainly students, were brought back to India from Ukraine at Government of India’s cost by 90 flights, of which 76 were commercial flights and 14 IAF flights in February and March 2022. Statement 2 is incorrect.
• Operation Indravati: The operation was launched in March 2024 to evacuate Indian nationals from Haiti amidst civil unrest. A total of 17 Indian nationals were safely evacuated from Haiti to Dominican Republic by helicopters. Statement 3 is incorrect.
Source: Ministry of External Affairs
Question 4
Governance | Schemes | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following with respect to PM Awaas Yojana – Urban:
- It is a Centrally sponsored scheme completely.
- A beneficiary family under the Mission comprises husband or wife only.
Which of the following statement is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
The Mission is implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) except the CLSS vertical of PMAY-U which is implemented as a Central Sector Scheme. Statement 1 is incorrect.
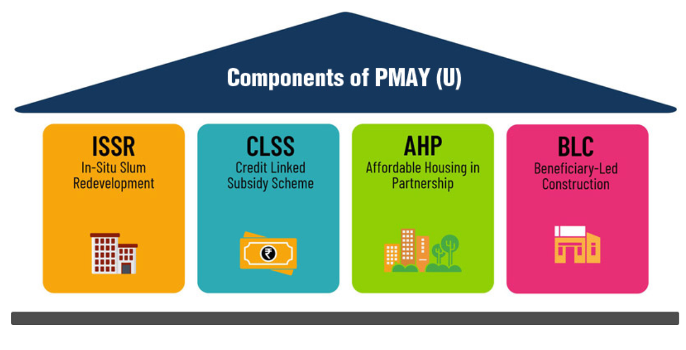
BENEFICIARY FAMILY
A beneficiary family under the Mission comprises husband, wife, unmarried sons and/or unmarried daughters. Statement 2 is incorrect.
The beneficiary family should not own a pucca house (an all-weather dwelling unit) either in his/her name or in the name of any member of his/her family in any part of India. An adult earning member (irrespective of marital status) is treated as a separate household provided that:
• He/she does not own a pucca (an all-weather dwelling unit) house in his/her name in any part of India.
• In case of a married couple, either of the spouses or both together in joint ownership will be eligible for a single house, subject to income eligibility of the household under the scheme. An eligible beneficiary can take advantage of only one of the four verticals of the Mission.
• Further, such a person with a pucca house having built-up area less than 21 sq.m may be included for enhancement of existing dwelling units up to 30 sq.m. However, if enhancement is not possible on account of lack of availability of land/space or any other reason, she/he may get a house under PMAY(U) elsewhere.
Question 5
International Relations | International Organisations | Medium | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following statements:
- UNOC in 2022 took place in Portugal.
- UNOC aims at catering SDG -12.
- UNOC needs 60 participating nations in order to implement the BBNJ agreement.
How many statements is or are correct?
A. Only one
B. Only two
C. All three
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (B) Only two
Detailed Explanation
UNOC 2022
Theme: Scaling up Ocean Action Based on Science and Innovation for the Implementation of SDG Goal 14: Stocktaking, Partnerships and Solutions. Statement 2 is incorrect.
The Ocean Conference, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world is seeking to address the many of the deep-rooted problems of our societies laid bare by the COVID-19 pandemic and which will require major structural transformations and common shared solutions that are anchored in the SDGs. Statement 1 is correct.
UNOC 2025
Theme: “Accelerating action and mobilizing all actors to conserve and sustainably use the ocean”.
The high-level 2025 United Nations Conference to Support the Implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 14: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development (the 2025 UN Ocean Conference) was held in Nice, France, from 9 – 13 June 2025, co-hosted by France and Costa Rica.
BBNJ Agreement
Purpose:
The BBNJ Agreement addresses the growing biodiversity crisis in the high seas, which are areas outside of any country’s exclusive economic zone (EEZ). It aims to protect marine life and ecosystems in these vast areas through measures like area-based management tools, environmental impact assessments, and the sharing of marine genetic resources.
Adoption and Entry into Force:
The agreement was adopted on June 19, 2023, after two decades of negotiations. It will enter into force 120 days after at least 60 countries ratify it. Statement 3 is correct.
India’s Status:
India signed the BBNJ Agreement in September 2024 and is currently in the process of ratifying it.
Question 6
International Relations | Places in news | Easy | Indian Express
SOURCE
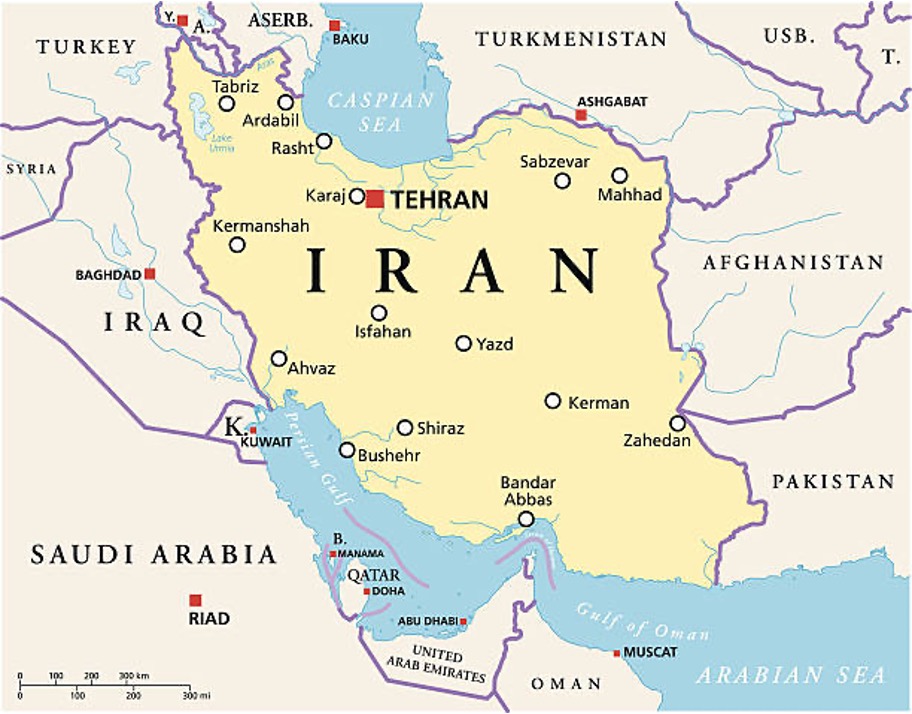
Which of the following does not border Iran?
A. Armenia
B. Pakistan
C. Georgia
D. Azerbaijan
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Georgia
Detailed Explanation
Question 7
Economy | GDP | Easy | Indian Express
SOURCE
Which of the following will not be impacted directly by revised GDP base year:
A. Index of Industrial Production
B. Consumer Price Index
C. Rate of Inflation
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (D) None of the above
Detailed Explanation
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is a crucial economic indicator in India that tracks the growth of various industrial sectors like mining, manufacturing, and electricity. It measures the short-term changes in the volume of production of a basket of industrial products during a given period compared to a base period. The Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) (now part of MoSPI) compiles and publishes the IIP monthly, providing insights into the industrial performance of the Indian Economy. This crucial indicator is directly linked to the production which is the core aspect of GDP.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. It’s a key indicator of inflation and is used to track the cost of living and make adjustments to wages, benefits, and tax brackets. CPI impacts price and inflation directly affects GDP.
The rate of inflation is the percentage increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a specific period, usually a year. It indicates how quickly prices are rising and how much the purchasing power of money is decreasing. Inflation is dependent on demand and supply which plays a key role in determining the price based on the product. Hence it impacts GDP too.
Question 8
Miscellaneous | Acts | Easy | The Hindu
SOURCE
Consider the following:
- The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act provides for unlimited monetary liability in India.
- The Atomic Energy Act restricts private companies from establishing nuclear power plants in India.
Which of the following statements is or are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
Solution & Detailed Explanation
Answer: (C) Both 1 and 2
Detailed Explanation
The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA), 2010
The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA), 2010, in India, establishes a legal framework for compensating victims of nuclear incidents and defines liability for nuclear damage. It aims to ensure prompt compensation to victims through a no-fault liability regime and facilitates India’s participation in the international nuclear liability regime.
Key aspects of the Act:
No-fault liability:
The operator of a nuclear installation is held liable for damages resulting from a nuclear incident, regardless of fault. Statement 1 is correct.
Liability limits:
The Act caps the operator’s liability for damages, currently at Rs 1,500 crore. If damages exceed this limit, the government is expected to intervene.
Right of recourse:
The Act allows the operator, after paying compensation, to seek recourse against suppliers in cases where the incident was caused by a supplier’s defective equipment or services.
Compensation mechanism:
The Act provides a mechanism for adjudicating claims and compensating victims through a Claims Commissioner and a Nuclear Damage Claims Commission.
Financial security:
The operator is required to maintain financial security, such as insurance, to cover potential liability.
International alignment:
The Act is designed to align with international conventions on nuclear liability, such as the Vienna Convention and the Paris Convention.
Time limit for claims:
The Act specifies a time limit for filing claims, which has been criticized as potentially inadequate for long-term damages.
Potential amendments:
There are ongoing discussions about amending the Act to address concerns regarding the liability of suppliers and to attract foreign investment in the nuclear energy sector
The Atomic Energy Act
The Atomic Energy Act, in general, refers to legislation that regulates the development, control, and use of atomic energy. In India, the Atomic Energy Act, 1962, specifically focuses on developing atomic energy for peaceful purposes and related matters. It provides the framework for controlling substances like uranium and thorium, and for establishing safety regulations for nuclear facilities and activities.
Key Aspects of the Indian Atomic Energy Act, 1962:
Purpose:
The Act aims to promote the peaceful development and use of atomic energy for the welfare of the Indian people.
Control over Substances:
It grants the Central Government control over substances like uranium and thorium, which can be used in atomic energy.
Reporting Requirements:
Individuals who discover or believe uranium or thorium deposits must report this to the Central Government.
Safety Regulations:
The Act, along with other rules and regulations, establishes a framework for ensuring safety in nuclear facilities and activities.
Regulatory Body:
The Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) is constituted under the Act to oversee and enforce safety regulations.
Offences and Penalties:
The Act outlines various offenses related to contravention of its provisions and prescribes penalties, including imprisonment and fines.
Other Important Points:
International Agreements:
The Act allows for international cooperation in peaceful uses of atomic energy.
Amendments:
The Act has been amended over time to address evolving needs and technologies.
Relationship with other Laws:
The Act is considered alongside other relevant laws like the Environmental Protection Act, 1986, and the Atomic Energy (Radiation Protection) Rules, 2004
Private Participation under the Act
The Atomic Energy Act, 1962, in India, does indeed restrict private sector participation in nuclear power generation, but it does not completely prohibit it. While the Act grants the government exclusive control over nuclear resources and their development, it does allow for exceptions and amendments.
Exclusive Control:
The Atomic Energy Act, 1962, primarily assigns the responsibility of nuclear power generation to the government, specifically to entities like the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL).
Limited Private Sector Involvement:
Although the Act initially prohibited private companies from directly operating nuclear power plants, it doesn’t completely exclude them from the sector. Statement 2 is correct.
Joint Ventures:
The Act has been amended to permit joint ventures between NPCIL and other public sector undertakings (PSUs). This allows for collaboration and resource sharing to facilitate nuclear projects, as seen with the formation of Anushakti Vidhyut Nigam Limited (ASHVINI).
Supply Chain Participation:
Private companies can participate in the nuclear power sector through the supply chain, providing goods and services, but not as direct operators of nuclear power plants







