52nd Constitutional Amendment Act 1985
- Added tenth Schedule to the Constitution and added disqualification of Legislators on grounds of defection.
61st Constitutional Amendment Act 1988
- Reduced the voting age from 21 years to 18 years for the Lok Sabha and state legislative assembly elections.
69th Constitutional Amendment Act 1991
- Designated the UT of Delhi as National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Provided for creation of 70 member legislative Assembly for Delhi.
- Article 239AA.
73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts 1992
- Granted constitutional status and protection to the panchayati raj institutions.
- For this purpose, the Amendment has added a new Part-IX entitled as “the panchayats” and a new Eleventh Schedule containing 29 functional items of the panchayats.
- Granted constitutional status and protection to the urban local bodies.
- For this purpose, the Amendment has added a new Part IX-A entitled as “the municipalities” and a new Twelfth Schedule containing 18 functional items of the municipalities
77th Constitutional Amendment Act 1995
- Reservation in Promotion in government jobs.
81st Constitutional Amendment Act 2000
- 50 percent ceiling not applicable on backlog vacancies.
84th Constitutional Amendment Act 2001
- Extended the freeze on readjustment of Lok Sabha seats upto 2026.
86th Constitutional Amendment Act
- Article 21-A – Elementary education a fundamental right
- Article 45 – State shall endeavour to provide early childhood care and education for all children until they complete the age of six years
- Article 51 –A – It shall be the duty of every citizen of India who is a parent or guardian to provide opportunities for education to his child or ward between the age of six and fourteen years
91st Constitutional Amendment Act 2003
- Total number of ministers not to exceed 15% of total strength of Lok Sabha/Assembly.
- MP/MLA who is disqualified under Anti defection will also be disqualified as a ministeror any remunerative political post.
- Exemption from disqualification in case of split by one third members of legislature party removed.
97th Constitutional Amendment Act 2011
- Gave a constitutional status and protection to cooperative societies. In this context, it made the following three changes in the constitution:
- It made the right to form co-operative societies a fundamental right.
- It included a new Directive Principle of State Policy on promotion of co-operative societies.
- It added a new Part IX-B in the constitution which is entitled as “The Co-operative Societies”.
99th Constitutional Amendment Act
- Replaced the collegium system of appointing judges to the Supreme Court and High Courts with a new body called the National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC).
- However, in 2015, the Supreme Court has declared this amendment act as unconstitutional and void. Consequently, the earlier collegium system became operative again.
100th Constitutional Amendment Act 2015
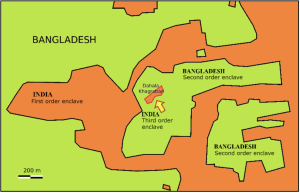
- Gave effect to the acquiring of certain territories by India and transfer of certain other territories to Bangladesh (through exchange of enclaves and retention of adverse possessions) in pursuance of the Land Boundary Agreement of 1974 and its Protocol of 2011
- Had to make changes in first schedule.
101st Constitutional Amendment Act 2016
- Conferred concurrent taxing powers upon the Parliament and the State Legislatures to makes laws for levying GST on every transaction of supply of goods or services or both.(Article 246 A)
- Dispensed the concept of “declared goods of special importance” under the constitution.
- Provided for the levy of Integrated GST on inter-state transactions of goods and services.
- Provided for the establishment of a Goods and Services Tax Council by a presidential order. (Article 279 A)
- Made the provision of compensation to the states for loss of revenue arising on account of introduction of GST for a period of five years.
- Substituted and ommitted certain entries in the Union and State Lists of the Seventh Schedule.
103rd Constitutional Amendment Act 2019
- Article 15(6) and Article 16(6)
104th Constitutional Amendment Act 2020
- Extended by ten years the deadline for the cessation of reservation of seats in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies for members of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. (Article 334)
➡️UPSC 2023 General Studies Course: https://sleepyclasses.com/general-studies-for-upsc/
➡️Sociology Optional for UPSC: https://sleepyclasses.com/sociology-for-upsc/
➡️Political Science and IR for UPSC: https://sleepyclasses.com/psir-for-upsc/
➡️Signup here – https://sleepyclasses.com/
Have any query related to UPSC preparation: 📞Contact Us ► Toll-Free: 1800 890 3043 ► Mobile: 6280133177 ► Email: [email protected] ► WhatsApp: 6280133177

